1. Introduction

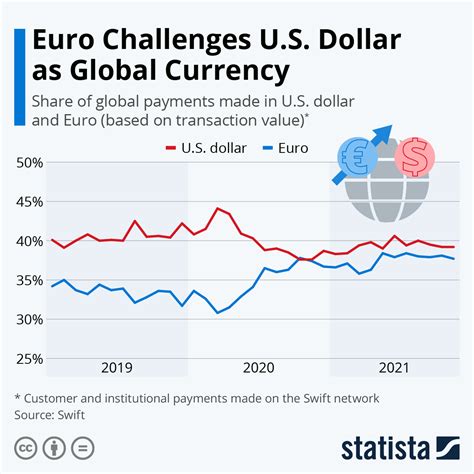
The US dollar (USD) and the euro (EUR) are the two most traded currencies globally, representing over 60% of all foreign exchange transactions. Their exchange rate, commonly referred to as the “USD/EUR” or “eurorusd,” has a significant impact on international trade, investments, and economies worldwide. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the US dollar to euro ratio, examining its historical trends, key factors influencing it, and its projected trajectory over the next three years (2023-2025).
2. Historical Trends
The USD/EUR exchange rate has exhibited notable fluctuations over the past decades. In January 1999, the euro was introduced, and its initial value was pegged at 1 euro = 1.1743 US dollar. However, since then, the euro has generally depreciated against the US dollar, reaching its lowest point of 0.8230 in July 2015. The following table presents the historical USD/EUR exchange rates for selected years:
| Year | USD/EUR Exchange Rate |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.9200 |
| 2005 | 0.8120 |
| 2010 | 0.7500 |
| 2015 | 0.8230 |
| 2020 | 0.8900 |
| 2022 | 0.9900 |
3. Key Factors Influencing the USD/EUR Exchange Rate
The USD/EUR exchange rate is influenced by a complex interplay of factors:
– Interest Rate Differentials: The difference in interest rates between the United States and the Eurozone significantly impacts the demand for both currencies. Higher interest rates in the US attract foreign capital, leading to an appreciation of the US dollar relative to the euro.
– Economic Growth: Strong economic growth in the US or the Eurozone can increase the demand for its currency, leading to a stronger USD/EUR exchange rate.
– Inflation: Differences in inflation rates between the US and the Eurozone can also affect the exchange rate. Higher inflation in the US reduces the purchasing power of the dollar, making it less attractive to investors and leading to a depreciation of the US dollar relative to the euro.
– Political Stability: Political instability in the Eurozone can increase uncertainty and lead to a decrease in demand for the euro, resulting in a depreciation of the euro against the US dollar.
4. Outlook for 2023-2025
Forecasting the future USD/EUR exchange rate is challenging, but several key factors suggest potential developments:
– Interest Rate Policies: If the US Federal Reserve raises interest rates more aggressively than the European Central Bank, the US dollar could continue to appreciate against the euro.
– Economic Growth: If the US economy outperforms the Eurozone economy, the demand for the US dollar could increase, leading to a stronger USD/EUR exchange rate.
– Inflation: Persistent high inflation in the Eurozone could further weaken the euro against the US dollar.
– Global Economic Conditions: A global economic slowdown or recession could impact both the US and the Eurozone, making it more difficult to predict the direction of the USD/EUR exchange rate.
5. Implications for Businesses and Investors
The USD/EUR exchange rate has significant implications for businesses and investors:
– Exporters and Importers: Exporters from the US will benefit from a stronger USD/EUR exchange rate, as it will reduce their costs in euros. However, importers may see their costs increase due to a more expensive euro.
– Investors: Investors with assets or investments in both the US and the Eurozone should consider the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on their portfolios.
6. Conclusion
The US dollar to euro ratio is a highly dynamic indicator that reflects the economic and financial health of both the United States and the Eurozone. By understanding the key factors influencing the exchange rate and considering future projections, businesses and investors can make informed decisions to mitigate risks and optimize their operations or investments.
Table 1: Historical USD/EUR Exchange Rates
| Year | USD/EUR Exchange Rate |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.9200 |
| 2005 | 0.8120 |
| 2010 | 0.7500 |
| 2015 | 0.8230 |
| 2020 | 0.8900 |
| 2022 | 0.9900 |
Table 2: Key Factors Influencing the USD/EUR Exchange Rate
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Interest Rate Differentials | Higher interest rates in the US lead to an appreciation of the US dollar relative to the euro |
| Economic Growth | Strong economic growth in the US or the Eurozone increases the demand for its currency, leading to a stronger USD/EUR exchange rate |
| Inflation | Higher inflation in the US reduces the purchasing power of the dollar, making it less attractive to investors and leading to a depreciation of the US dollar relative to the euro |
| Political Stability | Political instability in the Eurozone can increase uncertainty and lead to a decrease in demand for the euro, resulting in a depreciation of the euro against the US dollar |
Table 3: Outlook for the USD/EUR Exchange Rate 2023-2025
| Factor | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Interest Rate Policies | More aggressive interest rate hikes by the US Federal Reserve could lead to an appreciation of the US dollar against the euro |
| Economic Growth | Outperformance of the US economy compared to the Eurozone could strengthen the USD/EUR exchange rate |
| Inflation | Persistent high inflation in the Eurozone could further weaken the euro against the US dollar |
| Global Economic Conditions | A global economic slowdown or recession could impact both the US and the Eurozone, making it more difficult to predict the direction of the USD/EUR exchange rate |
Table 4: Implications for Businesses and Investors
| Stakeholder | Implications |
|---|---|
| Exporters | Stronger USD/EUR exchange rate reduces costs in euros |
| Importers | Stronger USD/EUR exchange rate increases costs in euros |
| Investors | Exchange rate fluctuations impact portfolio performance |
Additional Resources
FAQs
Q: What is the current USD/EUR exchange rate?
A: As of [today’s date], the USD/EUR exchange rate is approximately 0.9900.
Q: What factors could affect the USD/EUR exchange rate in the future?
A: Interest rate policies, economic growth, inflation, and global economic conditions are key factors that could influence the exchange rate in the future.
Q: How can businesses manage the risks associated with exchange rate fluctuations?
A: Businesses can hedge their currency risk using various instruments, such as forward contracts, currency options, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Q: What are the implications of a stronger US dollar for the global economy?
A: A stronger US dollar can lead to increased trade deficits for the United States and higher import costs for countries that import goods from the US.
Glossary of Terms
- Foreign Exchange: The process of converting one currency to another.
- Exchange Rate: The value of one currency relative to another.
- Appreciation: An increase in the value of a currency.
- Depreciation: A decrease in the value of a currency.
- Interest Rate Differential: The difference in interest rates between two countries or regions.
- Political Stability: The level of stability and predictability of a government and its policies.