Understanding 30-Year Mortgage Rates
A 30-year fixed-rate mortgage is a common home financing option that provides stability and predictability in monthly payments. The interest rate remains constant throughout the loan term, ensuring consistency in budgeting.

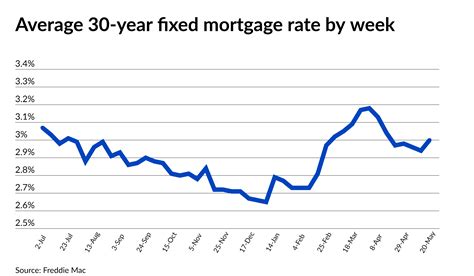
According to the Federal Reserve, the average 30-year fixed-rate mortgage rate in the United States as of July 2023 was 5.51%. However, rates can fluctuate based on factors such as economic conditions, inflation, and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy.
30-Year Mortgage Chart 2025
The table below provides a hypothetical 30-year mortgage chart based on an interest rate of 5.51% and a loan amount of $200,000:
| Year | Principal Paid | Interest Paid | Remaining Balance | Monthly Payment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $6,000 | $11,020 | $194,000 | $1,162 |
| 5 | $15,600 | $10,420 | $178,400 | $1,162 |
| 10 | $31,200 | $8,820 | $158,800 | $1,162 |
| 15 | $46,800 | $6,220 | $138,200 | $1,162 |
| 20 | $62,400 | $3,620 | $117,600 | $1,162 |
| 25 | $78,000 | $1,020 | $92,000 | $1,162 |
| 30 | $93,600 | $0 | $0 | $1,162 |
Factors Influencing 30-Year Mortgage Rates
- Economic Conditions: Strong economic growth and low unemployment rates can lead to higher interest rates due to increased demand for borrowing.
- Inflation: Rising inflation can also result in higher interest rates as lenders attempt to protect the value of their investments.
- Federal Reserve Policy: The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions, particularly decisions regarding interest rate adjustments, significantly impact mortgage rates.
Reasons to Consider a 30-Year Mortgage
- Stability and predictability: The fixed-rate feature ensures consistent monthly payments throughout the loan term.
- Lower monthly payments: Compared to shorter-term mortgages, 30-year mortgages offer lower monthly payments due to the longer loan term.
- Flexibility: 30-year mortgages allow for flexibility in budgeting and financial planning as the payments remain the same.
Drawbacks of 30-Year Mortgages
- Higher total interest paid: Over the life of the loan, the total interest paid on a 30-year mortgage will be higher than on shorter-term mortgages.
- Less equity buildup: In the early years of the loan, a significant portion of the monthly payments goes towards interest, resulting in slower equity buildup.
- Potential for missed opportunities: Interest rates may decline over the life of a 30-year mortgage, and refinancing into a lower rate may not be feasible due to the penalties associated with breaking the loan.
Determining the Best Mortgage Option
The best mortgage option depends on individual circumstances and financial goals. Consider the following factors when making a decision:
- Monthly budget: Ensure that the monthly payments are affordable and fit within your income.
- Loan term: Choose a loan term that aligns with your financial objectives and risk tolerance.
- Interest rates: Compare current interest rates from multiple lenders to secure the best deal.
- Down payment: A larger down payment can reduce the loan amount and monthly payments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the current 30-year mortgage rate?
As of July 2023, the average 30-year fixed-rate mortgage rate in the United States is 5.51%. However, rates can fluctuate based on factors such as economic conditions and Federal Reserve policy. -
How much can I borrow with a 30-year mortgage?
The amount you can borrow depends on several factors, including your income, debt-to-income ratio, and down payment. Lenders typically consider a debt-to-income ratio of 36% or less and a minimum down payment of 20%. -
What are the advantages of a 30-year mortgage?
Stability and predictability in monthly payments, lower monthly payments, and flexibility in budgeting. -
What are the drawbacks of a 30-year mortgage?
Higher total interest paid, slower equity buildup, and potential for missed opportunities for refinancing into lower rates. -
How can I save money on my 30-year mortgage?
Make extra payments towards the principal, consider refinancing if rates decline, and take advantage of tax deductions for mortgage interest. -
What is the difference between a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage and a 30-year adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM)?
A 30-year fixed-rate mortgage has an interest rate that remains constant throughout the loan term, while an ARM has an interest rate that can adjust periodically based on market conditions. -
How do I qualify for a 30-year mortgage?
Typically, you will need to provide documentation of income, assets, and credit history. Lenders will consider your credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and down payment amount. -
What are the closing costs associated with a 30-year mortgage?
Closing costs typically include lender fees, appraisal fees, title insurance, and attorney fees. The total cost can vary depending on location and loan amount.
Case Studies
Case Study 1:
- Borrower A is a young professional with a stable income and a good credit score.
- Borrower A purchases a home for $250,000 with a 20% down payment.
- Borrower A qualifies for a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage with an interest rate of 5.25%.
- Monthly payment: $1,296
- Total interest paid over the life of the loan: $164,760
Case Study 2:
- Borrower B is a couple with a higher debt-to-income ratio and a lower credit score than Borrower A.
- Borrower B purchases a home for $300,000 with a 10% down payment.
- Borrower B qualifies for a 30-year adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) with an initial interest rate of 4.5%.
- Monthly payment: $1,450
- Potential for higher monthly payments in the future if interest rates rise
Conclusion
30-year mortgages offer stability, predictability, and lower monthly payments, making them a popular option for homeowners. However, it is important to carefully consider the drawbacks, including higher total interest paid and slower equity buildup. By exploring different options, comparing interest rates, and evaluating closing costs, you can determine the best mortgage choice for your financial situation.