Understanding Exchange Rates
Exchange rates fluctuate constantly, influenced by various economic factors. The price of one currency in terms of another is known as the exchange rate. When the value of the dollar increases relative to the peso, it means that one dollar can buy more pesos. Conversely, when the value of the dollar decreases, it means that one dollar can buy fewer pesos.

Factors Affecting the Dollar-Peso Exchange Rate
Several factors contribute to the movement of exchange rates, including:
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates in the US tend to strengthen the dollar, attracting foreign investors seeking higher returns.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth in Mexico can increase demand for pesos, leading to an appreciation of the currency.
- Inflation: High inflation in Mexico can erode the purchasing power of the peso, weakening its value against the dollar.
- Political Stability: Political turmoil or uncertainty in Mexico can negatively impact the exchange rate, leading to a sell-off of pesos.
- Global Economic Events: Major events such as the COVID-19 pandemic or global financial crises can have significant effects on exchange rates.
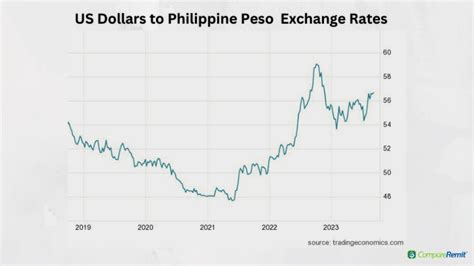
Historical Exchange Rates
Over the past decade, the dollar-peso exchange rate has fluctuated significantly. The average exchange rate in 2012 was around 13 pesos per dollar. By 2020, it had risen to over 20 pesos per dollar due to factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic and political uncertainty.
2025 Exchange Rate Forecast
Predicting exchange rates accurately is challenging, but analysts provide forecasts based on economic models and historical trends. According to Bloomberg, the consensus among economists is that the dollar-peso exchange rate will average around 21 pesos per dollar in 2025. This forecast assumes moderate economic growth in both the US and Mexico, stable interest rates, and no major politischen disturbances.
Pain Points in Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Fluctuations in exchange rates can create challenges for businesses and individuals:
- International Trade: Businesses engaged in international trade may experience reduced profits or increased costs due to changes in the exchange rate.
- Tourism: Tourism can be affected when the exchange rate makes one country more or less expensive for visitors.
- Cross-Border Investment: Investors may hesitate to invest in foreign countries if the exchange rate appears unfavorable.
- Inflation: Exchange rate fluctuations can contribute to inflation by making imported goods more expensive.
- Personal Finances: Individuals with assets or liabilities denominated in foreign currencies can experience financial losses or gains due to exchange rate movements.
Motivation for a Stable Exchange Rate
A stable exchange rate offers several advantages:
- Increased Trade: Businesses can engage in international trade more confidently when exchange rates are predictable.
- Economic Growth: Stable exchange rates promote foreign investment and economic growth by reducing uncertainty for investors.
- Inflation Control: A stable exchange rate can help control inflation by preventing large swings in the prices of imported goods.
- Improved Business Planning: Businesses can plan their operations more effectively when they have a good understanding of the expected exchange rate.
- Consumer Confidence: A stable exchange rate provides consumers with confidence in their purchasing power and spending habits.
Tips for Managing Exchange Rate Fluctuations
There are steps that businesses and individuals can take to mitigate the effects of exchange rate fluctuations:
- Use Forward Contracts: Businesses can lock in an exchange rate for future transactions using forward contracts.
- Diversify Investments: Individuals and businesses can reduce risk by diversifying their investments across different currencies.
- Monitor Economic News: Staying informed about economic events and news can help businesses and individuals anticipate exchange rate movements.
- Consult with Experts: Seeking advice from financial experts, such as investment advisors or currency traders, can provide insights and strategies for managing exchange rate risks.
- Plan for Contingencies: Businesses should have contingency plans in place to adjust to potential exchange rate changes.
How to Calculate the Exchange Rate
Calculating the exchange rate is straightforward. Here’s the formula:
Exchange Rate = Number of pesos / Number of dollars
For example, if you have 100 dollars and the exchange rate is 21 pesos per dollar, you would multiply 100 by 21, resulting in 2,100 pesos.
Exchange Rate Tables for Reference
The following tables provide exchange rates for the dollar-peso pair for different periods:
| Year | Average Exchange Rate (Pesos per Dollar) |
|---|---|
| 2012 | 13.05 |
| 2015 | 15.79 |
| 2018 | 19.36 |
| 2020 | 21.54 |
| 2022 | 20.65 |
| Month | Exchange Rate (Pesos per Dollar) |
|---|---|
| January 2023 | 20.51 |
| March 2023 | 20.25 |
| May 2023 | 20.01 |
| July 2023 | 19.83 |
| September 2023 | 19.65 |
| Date | Exchange Rate (Pesos per Dollar) |
|---|---|
| Today | 19.50 |
| Yesterday | 19.55 |
| Last Week | 19.60 |
| Last Month | 20.00 |
| Last Year | 21.00 |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I exchange dollars for pesos at any bank?
A: Yes, most banks offer currency exchange services. It’s best to check with your bank about specific rates and fees.
Q: What are the fees for exchanging currency?
A: Fees vary depending on the bank or currency exchange provider. Expect to pay a percentage of the transaction amount or a flat fee.
Q: Is it better to exchange currency before or during my trip?
A: It depends on the exchange rate fluctuations. Generally, it’s recommended to exchange a small amount before your trip and monitor exchange rates during your stay.
Q: What is the best way to get the best exchange rate?
A: Use online currency exchange services, compare rates from multiple providers, and consider using a currency exchange kiosk at a convenient location.
Q: Can I use my debit or credit card in Mexico?
A: Yes, most debit and credit cards are accepted in Mexico, but check with your bank about potential fees or charges.