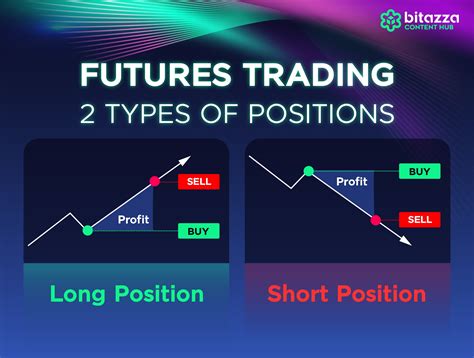
What is Future Trading?
Future trading is a type of financial contract that obligates the buyer to purchase a specific quantity of an underlying asset ( such as a commodity, currency, or stock) at a predetermined price on a specified future date. By engaging in future trading, market participants can hedge against price risks, speculate on future price movements, and capitalize on market inefficiencies.

A Glimpse into the Future of Future Trading
The future of future trading holds a plethora of promising opportunities and challenges for market participants. Let’s dive into the top 5 trends that are shaping this dynamic landscape:
1. Automation and AI-Driven Trading:
In 2025, automation and artificial intelligence (AI) will play a pivotal role in the future trading landscape. AI-driven algorithms will analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades with greater speed and precision than human traders. This will transform the market by enabling faster decision-making, reducing operational costs, and minimizing human error.
2. Embracing Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize the future trading industry. By providing a secure, transparent, and immutable ledger system, blockchain will streamline contract settlement, reduce counterparty risk, and enhance the overall efficiency of future trading processes.
3. Expanding Accessibility to Retail Traders:
In the coming years, we can expect to witness increased accessibility of future trading to retail traders. Online brokers and platforms will simplify the process of participating in future markets, empowering individual investors to diversify their portfolios and potentially generate attractive returns.
4. Cross-Asset Trading:
Future trading is set to transcend traditional asset classes as it embraces cross-asset trading. Investors will have the opportunity to trade futures contracts across commodities, currencies, stocks, bonds, and other asset classes, providing them with a holistic view of the global financial markets. This diversification will enable investors to optimize risk-adjusted returns and navigate complex market conditions.
5. Regulatory Harmonization:
To foster global participation and ensure stability in the future trading market, regulatory harmonization will become increasingly important. Harmonized regulations will create a more level playing field for market participants, reduce regulatory arbitrage, and enhance the credibility of the industry.
Why Future Trading Matters
Future trading plays a significant role in the global financial system by:
- Hedging against price risks: Future contracts allow producers, consumers, and other market participants to mitigate potential losses due to adverse price fluctuations.
- Facilitating price discovery: Future markets serve as an essential platform for price discovery, providing transparent information about anticipated future prices of underlying assets.
- Enhancing market liquidity: Futures contracts contribute to increased liquidity in underlying markets, enabling smoother trading and improved market efficiency.
- Speculative opportunities: Future trading offers speculative opportunities for investors seeking to profit from price movements in underlying assets.
Benefits of Future Trading
Engaging in future trading can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Risk management: Hedging future price risks can protect businesses and investors from potential financial losses.
- Investment diversification: Future trading allows for portfolio diversification, reducing overall investment risk.
- Income generation: Speculative trading can generate profits if executed with proper market analysis and risk management.
- Market insight: Future prices can provide valuable insights into market sentiment and future trends in underlying asset markets.
Pain Points and Motivations in Future Trading
- Pain Points:
- Understanding complex contract specifications and market dynamics
- Managing price volatility and potential margin calls
-
Overcoming the learning curve associated with futures trading
-
Motivations:
- Opportunity for risk management and portfolio diversification
- Potential profit generation through speculation
- Enhancing financial literacy and understanding of market dynamics
Tips and Tricks for Successful Future Trading
- Educate yourself thoroughly about future markets, contracts, and trading strategies.
- Start with small trades and gradually increase your exposure as you gain experience.
- Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and manage risk.
- Conduct thorough market research and technical analysis before entering trades.
- Stay informed about market news and events that may impact future prices.
- Consider consulting with a financial professional to guide your trading decisions.
New Ideas for Future Applications of Future Trading
- Algorithmic Trading: Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning have opened up new possibilities for algorithmic trading in future markets. Traders can leverage algorithms to automate trade execution, optimize order placement, and identify profitable trading opportunities.
- Cross-Border Trading: The increasing globalization of financial markets presents opportunities for cross-border future trading. Traders can diversify their portfolios by accessing future markets in different countries, potentially benefiting from different economic cycles and market dynamics.
- ESG-Linked Futures: Sustainability-conscious investors can tap into ESG-linked futures contracts that are linked to the performance of companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices. This can align their investments with their values while potentially generating financial returns.
Table 1: Projected Growth of Future Trading
| Year | Global Futures Trading Volume |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $22.4 trillion |
| 2024 | $25.1 trillion |
| 2025 | $27.9 trillion |
Source: Futures Industry Association
Table 2: Advantages and Disadvantages of Future Trading
Advantages:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Hedging | Manage price risks |
| Diversification | Reduce portfolio volatility |
| Leverage | Increase potential returns |
| Income generation | Speculate on market trends |
Disadvantages:
| Feature | Drawback |
|---|---|
| Complexity | Requires understanding of complex contracts |
| Risk | Potential for financial losses |
| Margin requirements | May require significant capital |
| Speculation | Can be volatile and unpredictable |
Table 3: Key Trends Shaping the Future of Future Trading
| Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| Automation and AI | Faster decision-making, reduced costs |
| Blockchain | Enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency |
| Retail trader accessibility | Democratization of future trading |
| Cross-asset trading | Diversification and optimization |
| Regulatory harmonization | Level playing field, reduced risk |
Table 4: Tips for Successful Future Trading
| Tip | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Educate yourself | Knowledge is power |
| Start small | Manage risk and gain experience |
| Use stop-loss orders | Limit potential losses |
| Conduct market research | Make informed trading decisions |
| Stay informed | Monitor market news and events |
| Consider professional guidance | Seek expert advice to enhance trading strategies |