Introduction
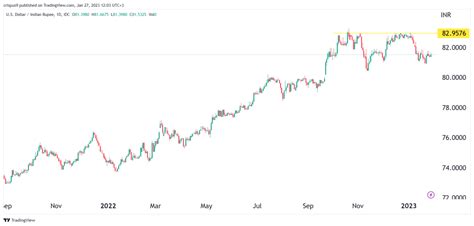
The Indian rupee (INR) has been on a downward trajectory against the US dollar (USD) in recent years, touching an all-time low of INR 83.29 to USD 1 in October 2023. This depreciation has had a significant impact on the Indian economy, leading to concerns about inflation, trade deficits, and foreign investment.

Factors Influencing Dollar-INR Exchange Rate
Numerous factors contribute to the fluctuations in the dollar-INR exchange rate, including:
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth in India, coupled with a widening trade deficit, has led to increased demand for the dollar.
- Interest rates: Interest rate differentials between India and the US also play a role. Higher interest rates in the US attract foreign investment, leading to a stronger dollar.
- Political stability: Political and economic stability in India can attract foreign investment and strengthen the rupee.
- Global economic conditions: Economic downturns or crises in other parts of the world can affect demand for the dollar and impact the INR.
Decline in INR Value
Over the past decade, the INR has depreciated by approximately 40% against the USD. This has been attributed to several factors, including:
- A widening trade deficit, with imports growing faster than exports.
- Reliance on imported oil and gas, making the country vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil prices.
- FPI outflows due to concerns over India’s economic outlook and rising inflation.
Impact of INR Depreciation
The depreciation of the INR has had various consequences for the Indian economy:
Inflation:
A weaker INR increases the cost of imported goods, leading to higher inflation.
Trade Deficit:
A depreciated INR makes exports cheaper and imports more expensive, potentially widening the trade deficit.
Foreign Investment:
A weaker INR can deter foreign investment, as it reduces the value of returns in dollar terms.
Forecast for 2025
Analysts and economists have varying forecasts for the dollar-INR exchange rate in 2025. Some predict a rebound in the rupee’s value, while others suggest a continued depreciation.
Rebound Scenario:
- Improved economic growth in India, leading to increased demand for the INR.
- Narrowing trade deficit as exports rise and imports stabilize.
- Stabilized global economic conditions reducing demand for the dollar.
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), India’s GDP is projected to grow by 7.2% in 2025, which could support a stronger INR.
Depreciation Scenario:
- Persistent trade deficit continues to put downward pressure on INR.
- Rising global inflation weakens the value of the INR.
- Geopolitical uncertainties and market volatility create a risk-off environment.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has estimated that the INR could depreciate to INR 90 to USD 1 by 2025, if current trends continue.
Implications for Businesses and Individuals
The trajectory of the dollar-INR exchange rate has significant implications for businesses and individuals:
Businesses:
- Exporters benefit from a stronger INR, as their products become cheaper in international markets.
- Importers face higher costs, which can impact their profitability.
- Foreign direct investment (FDI) may be affected by fluctuations in the exchange rate.
Individuals:
- Overseas travel and remittances become more expensive with a weaker INR.
- Foreign education or healthcare costs rise when the INR depreciates.
- Savings in USD may gain value against INR, but also carry currency risk.
Strategies to Mitigate Currency Risk
Businesses and individuals can employ strategies to mitigate currency risk:
- Hedging: Using financial instruments like forwards or options to lock in exchange rates.
- Invoice in foreign currencies: Exporters can invoice in USD or other strong currencies to minimize revenue losses.
- Diversify investments: Investing in global assets or hedging against currency fluctuations can reduce risk.
Conclusion
The forecast for the dollar-INR exchange rate in 2025 remains uncertain, with both rebound and depreciation scenarios possible. Understanding the factors influencing the exchange rate and implementing risk mitigation strategies are crucial for businesses and individuals to navigate the currency fluctuations. By keeping abreast of economic and market developments, stakeholders can make informed financial decisions and adapt to the evolving exchange rate landscape.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Assuming the INR will always depreciate: The INR has shown periods of appreciation in the past.
- Not hedging currency risk: Currency fluctuations can have significant financial impacts.
- Overreacting to short-term fluctuations: Exchange rates tend to fluctuate over time.
Why It Matters
The dollar-INR exchange rate significantly impacts the Indian economy and the financial decisions of businesses and individuals. Understanding the factors influencing the exchange rate and its potential implications is vital for mitigating risks and making informed financial choices.
Benefits of Hedging Currency Risk
- Predictability: Hedging provides certainty in exchange rates, reducing the impact of fluctuations.
- Risk management: Mitigation of potential losses due to currency depreciation.
- Improved cash flow: Stable exchange rates allow for better planning and budgeting.
- Competitive advantage: Hedging can enhance competitiveness for businesses in international markets.
FAQs
-
What is the historical trend of the dollar-INR exchange rate?
– The INR has depreciated by approximately 40% against the USD over the past decade. -
What factors influence the dollar-INR exchange rate?
– Economic growth, interest rates, political stability, and global economic conditions. -
What is the IMF’s forecast for India’s GDP growth in 2025?
– 7.2%. -
What is the RBI’s estimated depreciation of the INR by 2025?
– INR 90 to USD 1. -
How can individuals mitigate currency risk?
– Hedging, invoicing in foreign currencies, and diversifying investments. -
Why is it important to understand the dollar-INR exchange rate?
– It impacts India’s economy, trade, and financial decisions. -
What is the benefit of hedging currency risk?
– Predictability, risk management, improved cash flow, and competitive advantage. -
What common mistake should individuals avoid when dealing with currency fluctuations?
– Assuming the INR will always depreciate and not hedging currency risk.
Table 1: Historical Dollar-INR Exchange Rates
| Year | Average Rate (INR/USD) |
|---|---|
| 2013 | 61.67 |
| 2014 | 63.23 |
| 2015 | 64.72 |
| 2016 | 67.02 |
| 2017 | 64.93 |
| 2018 | 69.93 |
| 2019 | 71.73 |
| 2020 | 73.78 |
| 2021 | 74.20 |
| 2022 | 77.38 |
| 2023 | 81.02 |
Table 2: Factors Influencing Dollar-INR Exchange Rate
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Economic growth | Stronger growth leads to increased demand for INR. |
| Interest rates | Higher interest rates in India strengthen INR against USD. |
| Political stability | Stable political environment attracts investments and strengthens INR. |
| Global economic conditions | Economic downturns weaken the INR. |
Table 3: Impact of INR Depreciation
| Impact | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Inflation | Increased cost of imported goods, leading to higher inflation. |
| Trade deficit | Wider trade deficit as imports become more expensive. |
| Foreign investment | Deterred foreign investment due to reduced dollar returns. |
Table 4: Strategies to Mitigate Currency Risk
| Strategy | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Hedging | Using financial instruments to lock in exchange rates. |
| Invoice in foreign currencies | Exporting in USD or other strong currencies to reduce revenue loss. |
| Diversify investments | Investing globally or hedging against currency fluctuations. |