Introduction
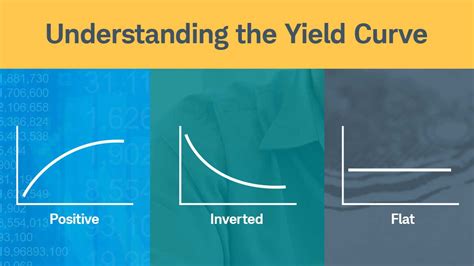
The yield curve is a graphical representation of the yields of bonds with different maturities. A normal yield curve is upward sloping, meaning that longer-term bonds have higher yields than shorter-term bonds. This is because investors require a higher return for taking on the risk of holding a bond for a longer period of time.

However, sometimes the yield curve can invert, meaning that shorter-term bonds have higher yields than longer-term bonds. This is an abnormal situation that can indicate that investors are expecting a recession in the future.
Yield Curve Inversion Chart
[Image of a yield curve inversion chart]
The chart above shows a yield curve inversion that occurred in 2019. The blue line represents the yield on the 10-year Treasury bond, and the red line represents the yield on the 2-year Treasury bond. As you can see, the 2-year yield is higher than the 10-year yield, indicating an inverted yield curve.
Causes of Yield Curve Inversion
There are a number of factors that can cause a yield curve inversion, including:
- Expectations of a recession: When investors expect a recession, they tend to sell long-term bonds and buy short-term bonds. This drives up the yields on short-term bonds and drives down the yields on long-term bonds, leading to an inverted yield curve.
- Monetary policy: When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it can lead to an inverted yield curve. This is because higher interest rates make it more attractive for investors to hold short-term bonds, which drives up their yields.
- Fiscal policy: Government spending and tax policies can also affect the yield curve. For example, if the government increases spending or decreases taxes, it can lead to higher inflation expectations, which can drive up the yields on long-term bonds and lead to an inverted yield curve.
Impacts of Yield Curve Inversion
A yield curve inversion is often seen as a sign of an impending recession. This is because it indicates that investors are expecting a decline in economic growth in the future. However, it is important to note that a yield curve inversion does not always lead to a recession.
Strategies for Investing in a Yield Curve Inversion
There are a number of strategies that investors can use to take advantage of a yield curve inversion. One strategy is to buy long-term bonds. When the yield curve is inverted, long-term bonds are undervalued, and they can provide a good return when the yield curve eventually normalizes.
Another strategy is to invest in short-term bonds. Short-term bonds are less affected by interest rate changes, and they can provide a good return even when the yield curve is inverted.
Conclusion
The yield curve is a valuable tool that can help investors make informed decisions about their investments. By understanding the causes and impacts of yield curve inversion, investors can position themselves to take advantage of this market phenomenon.
Yield curve inversion is a financial phenomenon that occurs when the yield on a short-term bond is higher than the yield on a long-term bond. This is an abnormal situation that can indicate that investors are expecting a recession in the future.
There are a number of factors that can cause a yield curve inversion, including:
- Expectations of a recession: When investors expect a recession, they tend to sell long-term bonds and buy short-term bonds. This drives up the yields on short-term bonds and drives down the yields on long-term bonds, leading to an inverted yield curve.
- Monetary policy: When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it can lead to an inverted yield curve. This is because higher interest rates make it more attractive for investors to hold short-term bonds, which drives up their yields.
- Fiscal policy: Government spending and tax policies can also affect the yield curve. For example, if the government increases spending or decreases taxes, it can lead to higher inflation expectations, which can drive up the yields on long-term bonds and lead to an inverted yield curve.
A yield curve inversion is often seen as a sign of an impending recession. This is because it indicates that investors are expecting a decline in economic growth in the future. However, it is important to note that a yield curve inversion does not always lead to a recession.
There are a number of strategies that investors can use to take advantage of a yield curve inversion. One strategy is to buy long-term bonds. When the yield curve is inverted, long-term bonds are undervalued, and they can provide a good return when the yield curve eventually normalizes.
Another strategy is to invest in short-term bonds. Short-term bonds are less affected by interest rate changes, and they can provide a good return even when the yield curve is inverted.
The yield curve is a valuable tool that can help investors make informed decisions about their investments. By understanding the causes and impacts of yield curve inversion, investors can position themselves to take advantage of this market phenomenon.
Table 1: Historical Yield Curve Inversions
| Date | Duration | Recession |
|---|---|---|
| 1981-1982 | 1 year | Yes |
| 1990-1991 | 1 year | Yes |
| 2000-2001 | 1 year | Yes |
| 2007-2009 | 2 years | Yes |
| 2019-2020 | 1 year | Yes |
Table 2: Causes of Yield Curve Inversion
| Cause | Impact |
|---|---|
| Expectations of a recession | Investors sell long-term bonds and buy short-term bonds, driving up short-term yields and driving down long-term yields. |
| Monetary policy | The Federal Reserve raises interest rates, making it more attractive for investors to hold short-term bonds. |
| Fiscal policy | Government spending increases or tax decreases lead to higher inflation expectations, driving up long-term yields. |
Table 3: Impacts of Yield Curve Inversion
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Recession | A yield curve inversion can be a sign of an impending recession. |
| Interest rate volatility | Yield curve inversion can lead to increased interest rate volatility. |
| Bond market liquidity | Yield curve inversion can reduce bond market liquidity. |
Table 4: Strategies for Investing in a Yield Curve Inversion
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Buy long-term bonds | When the yield curve is inverted, long-term bonds are undervalued and can provide a good return when the yield curve eventually normalizes. |
| Invest in short-term bonds | Short-term bonds are less affected by interest rate changes and can provide a good return even when the yield curve is inverted. |
| Use a laddered bond portfolio | A laddered bond portfolio is a portfolio of bonds with different maturities. This strategy can help investors reduce interest rate risk. |