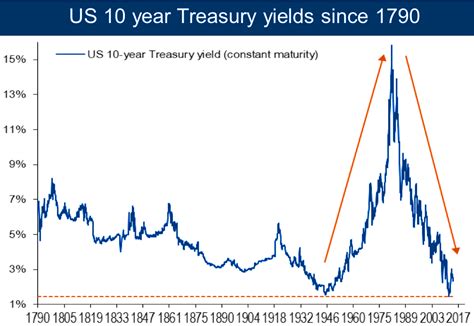
The 10-year U.S. Treasury rate is a crucial indicator that gauges the long-term health of the U.S. economy. Its movements impact various financial markets and play a significant role in investment decisions.

Understanding the 10-Year U.S. Treasury Rate
What is the 10-Year U.S. Treasury Rate?
The 10-year U.S. Treasury rate is the yield on a U.S. Treasury note that matures in 10 years. It is issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury to fund government spending. Investors purchase Treasury notes in exchange for a fixed return, which is the yield.
Factors Influencing the 10-Year U.S. Treasury Rate
Various factors influence the 10-year U.S. Treasury rate, including:
- Economic growth: A strong economy typically leads to higher interest rates as demand for borrowing increases.
- Inflation: Rising inflation pressures increase the cost of borrowing and lead to higher yields.
- Monetary policy: The Federal Reserve’s actions, such as interest rate adjustments, can significantly impact the Treasury rate.
- Fiscal policy: Government spending and tax policies can also influence the rate.
Historical Trends and Projections
Historical Performance
The 10-year U.S. Treasury rate has historically fluctuated over time. In the past, it has ranged from below 1% to over 15%. Since the 1980s, the yield has generally declined, reaching record lows in recent years.
Future Projections
Forecasting the future path of the 10-year U.S. Treasury rate is challenging, but economists make projections based on various factors. According to the Congressional Budget Office (CBO), the rate is expected to rise gradually over the next decade, reaching around 3.5% by 2030.
Market Implications and Applications
Impact on Financial Markets
The 10-year U.S. Treasury rate significantly impacts various financial markets:
- Bond market: The yield influences the pricing of other fixed-income investments, such as corporate bonds.
- Stock market: Rising yields can make stocks less attractive as investors shift towards safer investments.
- Mortgage market: Higher yields lead to increased mortgage rates, impacting homeownership costs.
Innovative Applications
Beyond its traditional uses, the 10-year U.S. Treasury rate can foster innovation in various ways:
- Risk management: The rate serves as a benchmark for assessing the risk of other investments.
- Macroeconomic forecasting: It provides insights into economic growth and inflation expectations.
- Tailoring financial products: Financial institutions can design products that cater to investors’ needs based on the Treasury rate.
Tables for Reference
| Year | 10-Year U.S. Treasury Rate |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 2.63% |
| 2015 | 2.17% |
| 2020 | 0.68% |
| 2022 | 2.95% |
| Year | CBO Projected Rate |
|---|---|
| 2025 | 3.1% |
| 2030 | 3.5% |
| 2035 | 3.7% |
| Sector | Impact |
|---|---|
| Bond market | Lower prices, higher yields |
| Stock market | Reduced valuations, increased volatility |
| Mortgage market | Higher mortgage rates, decreased affordability |
| Application | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Risk management | Provides a reference point for assessing risk |
| Macroeconomic forecasting | Enables predictions of economic growth and inflation |
| Tailoring financial products | Creates products that meet investor needs based on Treasury rate |
Conclusion
The 10-year U.S. Treasury rate is an important economic indicator that influences financial markets and plays a crucial role in investment decisions. Understanding its historical trends and future projections is essential for navigating market dynamics. Moreover, innovative applications of the Treasury rate can unlock new possibilities in risk management, macroeconomic forecasting, and financial product development. As the U.S. economy evolves, the 10-year Treasury rate will likely continue to be a significant force shaping the financial landscape.