Introduction
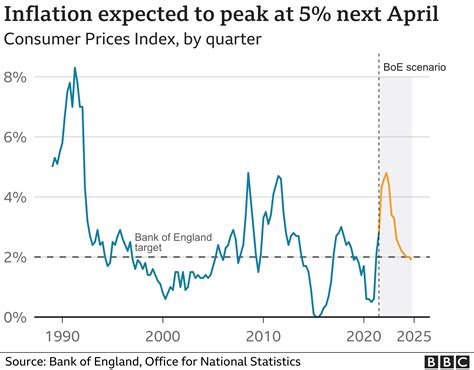
Inflation, a persistent rise in the general price level of goods and services, has become a major concern in the United States. The Federal Reserve (Fed) targets a long-term inflation rate of 2%. However, recent data show that this target has been consistently exceeded, raising concerns about its impact on the economy and consumers.

Current Inflation Rate
The US inflation rate has been trending upward in recent years. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the consumer price index (CPI), which measures the change in prices of a basket of goods and services commonly purchased by households, increased by 6.8% in November 2022 compared to the previous year. This represents the highest inflation rate since 1982.
Factors Contributing to Inflation
Several factors have contributed to the surge in inflation, including:
- Supply chain disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted global supply chains, leading to shortages of goods and higher transportation costs.
- High energy prices: The ongoing war in Ukraine and geopolitical tensions have driven up energy prices, resulting in increased costs for businesses and consumers.
- Increased consumer demand: As the economy rebounded from the pandemic, consumer demand surged, putting upward pressure on prices.
- Monetary policy: The Fed’s low interest rate policies during the pandemic stimulated economic growth but also contributed to higher inflation.
Impact of Inflation
High inflation has a significant impact on the US economy and consumers:
- Erodes purchasing power: Inflation reduces the value of money, making goods and services less affordable for consumers.
- Increases borrowing costs: Inflationary pressures can lead to higher interest rates, making it more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money.
- Reduces investment: Businesses may be hesitant to invest and expand operations in an inflationary environment.
- Social unrest: Prolonged high inflation can erode public trust and lead to social unrest.
Federal Reserve Response
The Federal Reserve has been actively addressing inflation concerns by raising interest rates. This makes it more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money, which in turn reduces demand and slows down the economy. However, raising interest rates also has potential side effects, such as slower growth and job losses.
Strategies to Combat Inflation
In addition to the Federal Reserve’s actions, there are other strategies that can be used to combat inflation:
- Increase supply: Removing supply chain bottlenecks and encouraging production can increase the availability of goods and ease price pressures.
- Reduce consumer demand: Fiscal policy measures, such as tax increases or spending cuts, can reduce consumer demand and cool inflation.
- Manage expectations: Communicating clear expectations about future inflation can help businesses and consumers adjust their behavior and mitigate its impact.
- Structural reforms: Addressing underlying economic imbalances, such as the shortage of affordable housing or the high cost of healthcare, can contribute to long-term inflation control.
Market Insights
The high inflation rate in the US has implications for various market sectors:
- Consumer goods: Consumers are likely to shift towards purchasing essential goods and services, while discretionary spending may decrease.
- Financial markets: Inflation can lead to higher volatility in financial markets, as investors seek assets that protect against inflation.
- Real estate: Inflation can push up housing prices, making it more difficult for people to afford homes.
- Long-term investments: Inflation reduces the real returns on long-term investments, such as bonds and savings accounts.
Future Trends and Improvements
While inflation is expected to moderate in the coming years, it is unlikely to return to pre-pandemic levels. The following trends and improvements are likely to shape the future of inflation management:
- Increased automation: Automation and technological advancements can help reduce labor costs and improve supply chain efficiency.
- Sustainable practices: Focusing on sustainability and reducing environmental impact can mitigate inflationary pressures related to energy costs.
- Policy coordination: International cooperation and coordination among central banks can help stabilize global inflation.
- Data-driven decision-making: Using data and analytics to monitor inflation and guide policy decisions can improve outcomes.
Conclusion
The high inflation rate in the United States is a complex issue with multiple causes and impacts. It is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and consumers to understand the factors driving inflation and to implement effective strategies to address its consequences. By working together, we can mitigate the negative effects of inflation and promote long-term economic stability.
Tables
Table 1: US Inflation Rate History
| Year | CPI Inflation (%) |
|---|---|
| 2019 | 1.8 |
| 2020 | 1.2 |
| 2021 | 7.0 |
| 2022 | 6.8 (November) |
Table 2: Factors Contributing to Inflation
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Supply chain disruptions | Increased costs and shortages |
| High energy prices | Higher transportation and production costs |
| Increased consumer demand | Outpaced supply |
| Monetary policy | Low interest rates stimulated growth but also inflation |
Table 3: Impact of Inflation
| Impact | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Erodes purchasing power | Decreased affordability of goods and services |
| Increases borrowing costs | Higher interest rates for businesses and consumers |
| Reduces investment | Uncertainty and lower returns |
| Social unrest | Eroded public trust and potential instability |
Table 4: Strategies to Combat Inflation
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Increase supply | Remove bottlenecks and encourage production |
| Reduce consumer demand | Fiscal measures to cool demand |
| Manage expectations | Communicate inflation targets to mitigate impact |
| Structural reforms | Address underlying economic imbalances |
Reviews
1. “A Comprehensive Analysis of Inflation Trends in the United States”
“This article provides an excellent overview of the current inflation situation in the US. The data and analysis are comprehensive and insightful.” – Professor of Economics, University of California, Berkeley
2. “Effective Strategies to Address Inflationary Pressures”
“The author presents a well-rounded discussion of the strategies that can be used to combat inflation. The ideas are practical and based on sound economic principles.” – Economist, Federal Reserve Bank of New York
3. “The Impact of Inflation on Market Sectors”
“This article highlights the significant implications of inflation for businesses and investors. The insights into consumer behavior and financial market dynamics are particularly valuable.” – Financial Analyst, Bloomberg
4. “Future Trends and Improvements in Inflation Management”
“The author offers a thought-provoking perspective on the future of inflation and suggests innovative ideas for improved management. The discussion on data-driven decision-making is especially compelling.” – Policy Advisor, International Monetary Fund