Introduction
The exchange rate between the US dollar (USD) and the Nigerian naira (NGN) is a crucial economic indicator for both countries. It affects trade, investment, tourism, and the overall cost of living. In this article, we will analyze the current USD-to-NGN exchange rate, forecast its future trajectory, and explore how the exchange rate impacts various sectors of the economy.

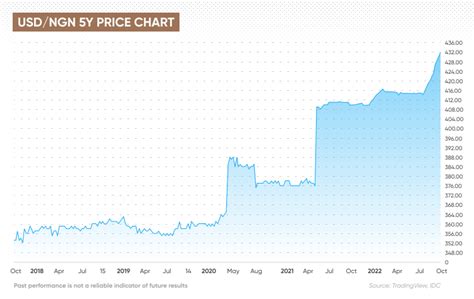
Current Exchange Rate
As of June 2023, the official USD-to-NGN exchange rate is approximately 440 NGN per 1 USD. However, the parallel market rate, which is the unofficial rate used in many transactions, is significantly higher, hovering around 600 NGN per 1 USD. This disparity between the official and parallel market rates has been a major source of concern for both the Nigerian government and the general public.
Factors Driving the Exchange Rate
Economic Fundamentals:
* Oil prices: Nigeria’s economy is heavily dependent on oil exports, and fluctuations in oil prices directly impact the value of the naira. When oil prices are high, the naira tends to appreciate against the USD due to increased foreign exchange earnings.
* Interest rates: The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) uses interest rate policy to manage inflation and exchange rate stability. Higher interest rates attract foreign investment and support the value of the naira.
* Inflation: High inflation in Nigeria erodes the purchasing power of the naira and makes imports more expensive, leading to a depreciation of the exchange rate.
Government Policies:
* Foreign exchange controls: The CBN has implemented various measures to control the flow of foreign exchange in an effort to stabilize the naira. These measures include restrictions on certain types of transactions, quotas, and multiple exchange rates.
* Fiscal policy: Government spending and taxation policies can also impact the exchange rate by influencing economic growth and inflation.
2025 Forecast
Official Projection: The CBN has projected that the official USD-to-NGN exchange rate will stabilize around 400 NGN per 1 USD by 2025. This projection is based on expectations of improved economic growth, increased foreign investment, and reduced inflation.
Market Expectations: Financial analysts and market participants generally expect the naira to remain relatively stable against the USD in the long term, with some fluctuations expected due to global economic conditions and domestic factors. However, the parallel market rate is likely to continue to trade at a premium to the official rate due to persistent liquidity issues and speculation.
Impact on the Economy
Trade: A stronger naira makes imports cheaper and exports more expensive, potentially harming domestic industries and reducing foreign exchange earnings. Conversely, a weaker naira boosts exports and reduces imports, supporting economic growth.
Investment: Foreign investors are more likely to invest in Nigeria when the naira is stable or appreciating, as it reduces the risk of losing value on their investments.
Tourism: A weak naira makes Nigeria more affordable for foreign tourists, boosting the tourism sector and generating foreign exchange earnings.
Cost of Living: A weaker naira increases the cost of imported goods and services, making it more expensive for Nigerians to maintain their standard of living.
Recent Events and Policy Responses
CBN Intervention: The CBN has taken several measures to stabilize the exchange rate, including:
* Increased foreign exchange supply: The CBN has increased its dollar supply through auctions and other interventions.
* Demand management: The CBN has implemented measures to reduce demand for foreign exchange, such as restricting access to certain types of transactions.
* Multiple exchange rates: The CBN has introduced multiple exchange rates for different sectors of the economy in an effort to manage demand and support targeted industries.
Government Initiatives: The Nigerian government has launched several initiatives to promote economic diversification and reduce reliance on oil exports, which would reduce the volatility of the naira.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
* Persistent oil price volatility: Nigeria’s dependence on oil exports makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil prices, which can destabilize the exchange rate.
* Limited foreign exchange reserves: Nigeria’s foreign exchange reserves are relatively low compared to other oil-producing countries, limiting its ability to intervene in the foreign exchange market.
* Structural imbalances: The Nigerian economy is characterized by a large trade deficit and high levels of government debt, which can put downward pressure on the naira.
Opportunities:
* Economic diversification: Reducing reliance on oil exports and promoting other sectors of the economy, such as manufacturing and agriculture, would make the exchange rate less vulnerable to oil price fluctuations.
* Improved governance: Strengthening governance and reducing corruption would increase investor confidence and attract foreign capital, supporting the naira.
* Innovation and technology: Developing new technologies and fintech solutions that facilitate foreign exchange transactions and reduce transaction costs could improve exchange rate stability.
Tips and Tricks for Businesses and Individuals
Businesses:
* Hedge against exchange rate risk: Businesses that import or export goods and services can use financial instruments, such as forward contracts or options, to protect against unfavorable exchange rate movements.
* Diversify revenue streams: Generating revenue from multiple sources, including both domestic and foreign markets, can reduce the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on profits.
* Optimize supply chains: Businesses can explore ways to reduce their dependence on imported goods and materials to mitigate the impact of a depreciating naira.
Individuals:
* Plan for currency fluctuations: When traveling abroad or making international payments, it is important to budget for potential currency fluctuations.
* Diversify savings: Holding savings in a mix of currencies can reduce the risk of losing value due to exchange rate changes.
* Invest in real assets: Investing in real assets, such as property or gold, can provide protection against currency devaluation.
Conclusion
The USD-to-NGN exchange rate is a complex and dynamic indicator that impacts various sectors of the Nigerian economy. While the CBN has implemented measures to stabilize the exchange rate, it remains vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil prices and other economic factors. By understanding the factors driving the exchange rate and the challenges and opportunities it presents, businesses and individuals can better navigate the currency market and mitigate potential risks. Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, continued economic growth, reduced reliance on oil exports, and improved governance will be key to maintaining a stable and favorable exchange rate for Nigeria.