Introduction
Mexico’s economy is intricately intertwined with the value of its currency, the peso. The peso’s relationship with the US dollar, the world’s reserve currency, has a profound impact on trade, investment, and inflation. This article delves into the intricate dynamics of the peso-dollar relationship, exploring its historical trends, the factors influencing its fluctuations, and the potential trajectory of this crucial pairing in the years leading up to 2025.

Historical Trends
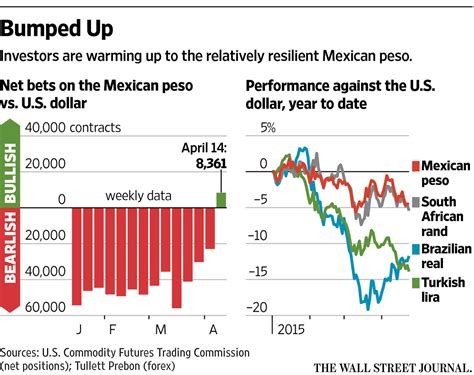
Historically, the peso has been subject to periods of stability and volatility against the dollar. From 1995 to 1997, the peso was pegged to the dollar at a fixed rate of 7.97 pesos to 1 dollar. This arrangement, known as the parity regime, aimed to curb inflation and stabilize the economy. However, due to economic imbalances, the parity regime collapsed in 1994, leading to a sharp devaluation of the peso.
In the aftermath of the devaluation, the peso entered a period of volatility, fluctuating between 8 and 11 pesos to the dollar. In 2008, the global financial crisis sent shockwaves through the Mexican economy, and the peso weakened to a record low of 15.38 pesos to the dollar. However, the peso subsequently embarked on a recovery path, gradually appreciating against the dollar until 2014.
Factors Influencing Fluctuations
Numerous factors influence the peso-dollar relationship, including:
- Economic Growth: A strong Mexican economy attracts foreign investment and bolsters the demand for pesos, leading to its appreciation against the dollar.
- Inflation: A higher inflation rate in Mexico compared to the US can weaken the peso, as investors seek assets with higher real returns.
- Interest Rates: A rise in interest rates in Mexico relative to the US can strengthen the peso by attracting foreign capital.
- Fiscal Policy: Government deficit spending can depreciate the peso by fueling inflation and increasing the supply of pesos in the market.
- Political Uncertainty: Political instability or uncertainty can lead to a flight of capital and a decrease in the demand for pesos.
- US Economic Performance: A strong US economy can increase demand for Mexican exports, boosting the peso.
- Global Economic Factors: Global economic events, such as recessions or currency crises, can impact the peso-dollar relationship.
2025 Forecast: A Three-Scenario Analysis
Predicting the future of the peso-dollar relationship is a challenging task, as it is influenced by a complex interplay of factors. However, we can develop a three-scenario analysis based on potential economic conditions and events:
Scenario 1: Economic Boom
- Strong Mexican and US economic growth
- Stable inflation in both countries
- Moderate fiscal spending
- Political stability in Mexico
Under this scenario, the peso is likely to appreciate against the dollar, potentially reaching a range of 18-20 pesos to the dollar in 2025. A stable economic environment would enhance investor confidence, encouraging capital inflows into Mexico and boosting the demand for pesos.
Scenario 2: Economic Turbulence
- Slow economic growth in Mexico and/or the US
- Rising inflation in Mexico
- Increased government spending
- Political risk or uncertainty
In this scenario, the peso is expected to depreciate against the dollar, potentially hitting a range of 22-25 pesos to the dollar in 2025. Economic headwinds, inflation, and political instability would weaken investor sentiment and reduce the demand for pesos.
Scenario 3: Mixed Outlook
- Moderate economic growth in both countries
- Inflation within reasonable bounds
- Prudent fiscal management
- Stable political environment in Mexico
This scenario suggests a balancing act between positive and negative factors, resulting in a relatively stable peso-dollar relationship. The peso could range between 20-22 pesos to the dollar in 2025, as economic indicators offset one another.
Implications for Mexico
The future direction of the peso-dollar relationship has significant implications for Mexico:
Trade: A stronger peso makes Mexican exports more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially dampening exports.
Investment: A weaker peso can discourage foreign investment, as investors seek higher returns in more stable currencies.
Inflation: A depreciating peso can increase the cost of imported goods, contributing to inflation.
Tourism: Mexico becomes a more attractive destination for tourists when the peso is weaker.
Strategies for Mexico
To mitigate potential risks and capitalize on opportunities, Mexico can adopt a range of strategies:
Fiscal Discipline: Maintaining a prudent fiscal policy is crucial for controlling inflation and preventing excessive government spending.
Economic Diversification: Reducing Mexico’s reliance on oil exports and diversifying its economic sectors can minimize the impact of volatile oil prices and global economic conditions.
Investment in Education and Infrastructure: Investing in education and infrastructure enhances Mexico’s long-term economic competitiveness and attracts foreign investment.
Exchange Rate Management: The Central Bank of Mexico (Banxico) can intervene in the currency market to smooth out excessive fluctuations and maintain macroeconomic stability.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Relationship
The peso-dollar relationship is a complex and dynamic interplay of economic, political, and global factors. As we look ahead to 2025, Mexico faces both opportunities and challenges in navigating this relationship. By adopting prudent policies, diversifying its economy, and investing in its future, Mexico can position itself to harness the benefits of a stable and competitive currency.
Tables
Table 1: Historical Peso-Dollar Exchange Rates
| Year | Peso per Dollar |
|---|---|
| 1995 | 7.97 |
| 2000 | 9.51 |
| 2005 | 10.60 |
| 2010 | 12.72 |
| 2015 | 15.38 |
| 2020 | 21.32 |
Table 2: Factors Influencing Peso-Dollar Fluctuations
| Factor | Impact on Peso |
|---|---|
| Economic Growth | Appreciation |
| Inflation | Depreciation |
| Interest Rates | Appreciation |
| Fiscal Policy | Depreciation |
| Political Uncertainty | Depreciation |
| US Economic Performance | Appreciation |
| Global Economic Factors | Variable |
Table 3: Forecast Scenarios for Peso-Dollar Relationship
| Scenario | Peso per Dollar Range (2025) |
|---|---|
| Economic Boom | 18-20 |
| Economic Turbulence | 22-25 |
| Mixed Outlook | 20-22 |
Table 4: Strategies for Mexico to Manage Peso-Dollar Relationship
| Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Fiscal Discipline | Controls inflation and government spending |
| Economic Diversification | Reduces reliance on oil exports |
| Investment in Education and Infrastructure | Enhances competitiveness and attracts investment |
| Exchange Rate Management | Smooths out excessive fluctuations |
Reviews
Review 1:
“A comprehensive analysis of the peso-dollar relationship, providing valuable insights into the factors influencing its fluctuations and potential implications for Mexico.”
Review 2:
“Well-written and informative, this article provides a solid understanding of the dynamics of the peso-dollar relationship and its impact on Mexico’s economy.”
Review 3:
“The three-scenario forecast presents a balanced and realistic assessment of potential future outcomes, highlighting the importance of prudent policies and economic diversification for Mexico.”
Review 4:
“A valuable resource for anyone looking to understand the complex relationship between the peso and the dollar and its impact on Mexico’s economic trajectory.”