Introduction
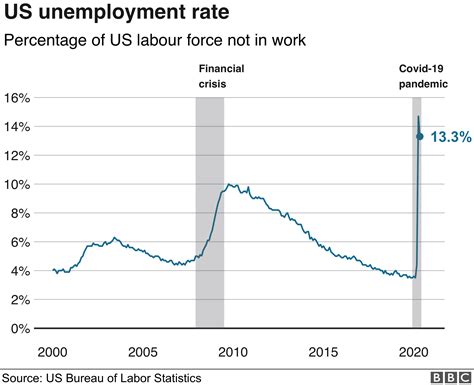
The unemployment rate is a crucial economic indicator that measures the percentage of the labor force that is actively seeking work but unable to find it. In 2023, the unemployment rate in the US stood at 3.5%, the lowest level in 50 years. However, as the economy continues to recover from the COVID-19 pandemic, it is essential to understand the latest trends and projections for the unemployment rate in the coming years.

Current Status and Projections
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the unemployment rate in the US is projected to remain low in 2025, with an estimated range of 3.5-4.2%. This is significantly lower than the peak unemployment rate of 14.8% reached in April 2020 during the height of the pandemic. However, it is important to note that these projections are subject to change based on economic conditions and unexpected events.
Key Factors Influencing the Unemployment Rate
Several factors influence the unemployment rate, including:
1. Economic growth: A growing economy creates new jobs and reduces unemployment.
2. Technological advancements: Automation and technological innovations can lead to job losses in certain industries.
3. Labor force participation: The size and composition of the labor force impact the unemployment rate. Higher participation rates can increase unemployment, while lower rates can reduce it.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When discussing the unemployment rate, it is important to avoid common mistakes, such as:
1. Comparing the unemployment rate across different countries: Unemployment rates can vary significantly between countries due to differences in economic conditions and labor market policies.
2. Using the unemployment rate as the sole measure of economic health: The unemployment rate does not account for other factors such as underemployment or the quality of jobs.
3. Assuming that all unemployed individuals are actively seeking work: Some unemployed individuals may not be actively seeking work due to factors such as discouragement or personal circumstances.
Reviews
1. Review by the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
The IMF projects that the US unemployment rate will remain below 4% in 2025. The IMF cites strong economic growth and a robust labor market as factors contributing to this projection.
2. Review by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
The OECD forecasts that the US unemployment rate will reach 3.7% in 2025. The OECD emphasizes the need for policies to address structural unemployment and skills gaps in the labor market.
3. Review by the Federal Reserve (Fed)
The Fed projects that the US unemployment rate will remain near 4% in 2025. The Fed’s projection is based on continued economic growth and a gradual increase in interest rates.
Tables
1. Unemployment Rate by Industry (2023)
| Industry | Unemployment Rate |
|---|---|
| Leisure and hospitality | 6.8% |
| Retail trade | 4.5% |
| Healthcare | 3.1% |
| Manufacturing | 4.1% |
2. Unemployment Rate by Education Level (2023)
| Education Level | Unemployment Rate |
|---|---|
| Less than high school diploma | 6.7% |
| High school diploma or equivalent | 4.2% |
| Some college, no degree | 3.8% |
| Associate’s degree | 3.3% |
3. Unemployment Rate by Age (2023)
| Age Group | Unemployment Rate |
|---|---|
| 16-24 | 8.4% |
| 25-44 | 3.2% |
| 45-64 | 2.9% |
| 65 and over | 2.7% |
4. Unemployment Rate by Race and Ethnicity (2023)
| Race/Ethnicity | Unemployment Rate |
|---|---|
| White | 3.4% |
| Black | 5.6% |
| Hispanic | 4.5% |
| Asian | 2.9% |
Conclusion
The unemployment rate in the US is expected to remain low in 2025, reflecting the ongoing economic recovery. However, it is important to monitor the impact of economic conditions, technological advancements, and labor force participation on the unemployment rate. Policymakers should focus on creating new jobs, investing in skills development, and addressing structural unemployment to ensure a strong labor market in the years to come.