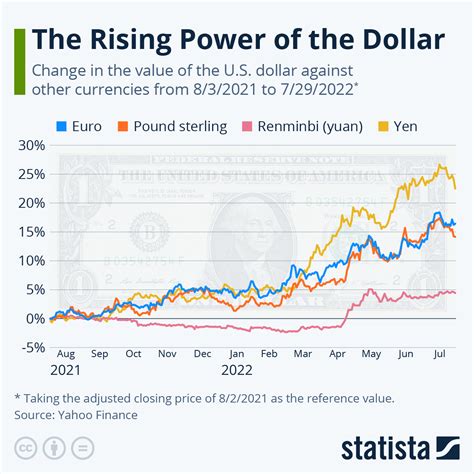
Introduction: The Rise of the USD Dollar in India

The Indian rupee (INR) has been experiencing significant volatility against the US dollar (USD) in recent years. This has led to growing concerns about the future of the Indian currency and the impact it will have on the Indian economy. In this article, we will explore the factors driving the rise of the USD dollar in India, its implications for the country, and possible measures that can be taken to address the situation.
Factors Driving the Rise of the USD Dollar in India
Several factors have contributed to the rise of the USD dollar in India:
- Current Account Deficit: India has been running a persistent current account deficit (CAD) for several years. This means that the value of India’s imports exceeds the value of its exports. To finance this deficit, India needs to borrow foreign currency, which puts upward pressure on the USD dollar.
- Foreign Institutional Investment (FII): FIIs are foreign investors who invest in Indian stocks and bonds. When FIIs sell their investments and repatriate their funds, it creates demand for USD, leading to an appreciation of the dollar.
- Global Economic Conditions: The global economy has been slowing down in recent years, which has led to a flight to safety by investors. This has resulted in increased demand for the USD, which is seen as a safe haven currency.
- US Monetary Policy: The US Federal Reserve has been raising interest rates in an effort to combat inflation. This has made the USD more attractive to investors, as it offers higher returns.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty: The ongoing war in Ukraine and other geopolitical tensions have created uncertainty in the global markets. This has led to increased demand for the USD, which is seen as a stable currency in times of uncertainty.
Implications for India
The rise of the USD dollar has several implications for India:
- Inflation: A stronger USD dollar can lead to higher inflation in India, as imported goods become more expensive.
- Economic Growth: A weaker INR can make Indian exports less competitive, which can slow down economic growth.
- Foreign Debt: India has a significant amount of foreign debt denominated in USD. A stronger USD dollar can make it more expensive for India to repay its debt.
- Foreign Exchange Reserves: India’s foreign exchange reserves are used to support the value of the INR. A stronger USD dollar can deplete India’s foreign exchange reserves.
Measures to Address the Situation
The Indian government and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) have taken several measures to address the rise of the USD dollar:
- Curbing CAD: The government is taking steps to reduce the CAD by increasing exports and reducing imports.
- Attracting FII: The government is offering incentives to FIIs to invest in India.
- Managing Inflation: The RBI is using monetary policy tools to control inflation.
- Building Foreign Exchange Reserves: The RBI is purchasing USD from the market to build up India’s foreign exchange reserves.
Case Studies
1. China: China has successfully managed to stabilize its currency against the USD by controlling capital flows and intervening in the foreign exchange market.
2. Brazil: Brazil has used a combination of monetary policy and fiscal policy to reduce its CAD and stabilize its currency against the USD.
Lessons for India
India can learn from the experiences of China and Brazil to develop strategies to address the rise of the USD dollar:
- Strengthen Export Competitiveness: India can invest in infrastructure and technology to improve the competitiveness of its exports.
- Reduce CAD: India can take steps to reduce its dependence on imports and increase its exports.
- Attract Foreign Investment: India can create a more conducive environment for foreign investment by reducing bureaucracy and improving the ease of doing business.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead
The rise of the USD dollar in India is a complex issue with multiple factors contributing to it. The Indian government and the RBI are taking steps to address the situation, but it remains to be seen whether these measures will be successful in stabilizing the INR. It is important for India to develop a long-term strategy to manage the volatility of its currency and reduce its dependence on the USD dollar.
Table 1: Factors Driving the Rise of the USD Dollar in India
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Current Account Deficit | India’s imports exceed its exports, leading to a demand for USD to finance the deficit. |
| Foreign Institutional Investment (FII) | When FIIs sell their investments in India and repatriate their funds, it creates demand for USD. |
| Global Economic Conditions | A slowing global economy leads to a flight to safety, increasing demand for the USD. |
| US Monetary Policy | Interest rate hikes by the US Federal Reserve make the USD more attractive to investors. |
| Geopolitical Uncertainty | The war in Ukraine and other geopolitical tensions create uncertainty, leading to increased demand for the USD. |
Table 2: Implications of the Rise of the USD Dollar for India
| Implication | Description |
|---|---|
| Inflation | A stronger USD dollar can lead to higher inflation in India as imported goods become more expensive. |
| Economic Growth | A weaker INR can make Indian exports less competitive, slowing down economic growth. |
| Foreign Debt | India has significant foreign debt denominated in USD. A stronger USD dollar can make it more expensive for India to repay its debt. |
| Foreign Exchange Reserves | India’s foreign exchange reserves are used to support the value of the INR. A stronger USD dollar can deplete India’s foreign exchange reserves. |
Table 3: Measures to Address the Rise of the USD Dollar in India
| Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Curbing CAD | The government is taking steps to reduce the CAD by increasing exports and reducing imports. |
| Attracting FII | The government is offering incentives to FIIs to invest in India. |
| Managing Inflation | The RBI is using monetary policy tools to control inflation. |
| Building Foreign Exchange Reserves | The RBI is purchasing USD from the market to build up India’s foreign exchange reserves. |
Table 4: Case Studies of Currency Stabilization
| Country | Strategy | Results |
|---|---|---|
| China | Controlled capital flows and intervened in the foreign exchange market | Stabilized its currency against the USD |
| Brazil | Used a combination of monetary policy and fiscal policy | Reduced its CAD and stabilized its currency against the USD |