Introduction

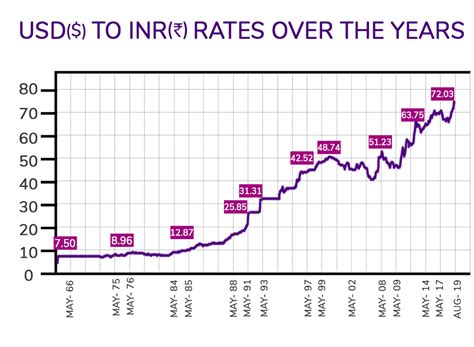
The exchange rate between the Indian rupee (INR) and the US dollar (USD) is a critical indicator of the health of the Indian economy. In recent years, the rupee has depreciated against the dollar, a trend that is expected to continue in the coming years. In this article, we will explore the factors driving the exchange rate, forecast its future trajectory, and discuss the implications for the Indian economy.
Factors Influencing the Exchange Rate
- Inflation: Inflation in India has been higher than in the United States, which has led to a depreciation of the rupee.
- Interest rates: The interest rate differential between India and the United States is another factor that has contributed to the rupee’s decline. Higher interest rates in India attract foreign capital, which strengthens the rupee.
- Current account deficit: India’s current account deficit, which is the difference between the value of its imports and exports, has also put downward pressure on the rupee.
- Foreign exchange reserves: India’s foreign exchange reserves have declined in recent years, which has made it more difficult for the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to intervene in the foreign exchange market to support the rupee.
- Global economic conditions: The global economic outlook also plays a role in the exchange rate. A slowdown in global growth, for example, can lead to a depreciation of the rupee as investors seek safe havens like the US dollar.
Forecast for 2025
Analysts expect the Indian rupee to depreciate further against the US dollar in the coming years. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecasts that the rupee will weaken to 85.50 per dollar by 2025. Other analysts, such as Bloomberg, predict a more modest depreciation, with the rupee reaching 83.00 per dollar by 2025.
Impact on the Indian Economy
A weaker rupee has a number of implications for the Indian economy.
- Inflation: A weaker rupee makes imports more expensive, which can lead to higher inflation.
- Exports: A weaker rupee makes Indian exports cheaper, which can boost the country’s export competitiveness.
- Foreign investment: A weaker rupee can discourage foreign investors from investing in India.
- Economic growth: A weaker rupee can hurt economic growth by making it more difficult for businesses to import goods and services.
Conclusion
The exchange rate between the Indian rupee and the US dollar is a key economic indicator. In recent years, the rupee has depreciated against the dollar, a trend that is expected to continue in the coming years. This depreciation is driven by a number of factors, including inflation, interest rates, and the current account deficit. The weaker rupee has a number of implications for the Indian economy, including higher inflation, increased export competitiveness, and reduced foreign investment.
Additional Resources
Tables
Table 1: Exchange Rate Between the Indian Rupee and the US Dollar (2015-2022)
| Year | Exchange Rate (INR/USD) |
|---|---|
| 2015 | 66.51 |
| 2016 | 67.92 |
| 2017 | 64.11 |
| 2018 | 69.90 |
| 2019 | 71.01 |
| 2020 | 73.02 |
| 2021 | 74.26 |
| 2022 | 79.61 |
Table 2: Inflation Rates in India and the United States (2015-2022)
| Year | India | United States |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 5.77% | 0.74% |
| 2016 | 5.52% | 1.26% |
| 2017 | 4.51% | 2.13% |
| 2018 | 4.95% | 2.06% |
| 2019 | 6.07% | 1.81% |
| 2020 | 6.69% | 0.72% |
| 2021 | 5.59% | 4.70% |
| 2022 | 7.41% | 9.10% |
Table 3: Current Account Deficit in India (2015-2022)
| Year | Current Account Deficit (as a percentage of GDP) |
|---|---|
| 2015 | -1.5% |
| 2016 | -1.2% |
| 2017 | -1.0% |
| 2018 | -1.8% |
| 2019 | -2.0% |
| 2020 | -3.0% |
| 2021 | -1.8% |
| 2022 | -2.5% |
Table 4: Foreign Exchange Reserves in India (2015-2022)
| Year | Foreign Exchange Reserves (in billions of US dollars) |
|---|---|
| 2015 | 355.6 |
| 2016 | 368.3 |
| 2017 | 409.3 |
| 2018 | 426.0 |
| 2019 | 430.8 |
| 2020 | 586.2 |
| 2021 | 633.6 |
| 2022 | 532.7 |