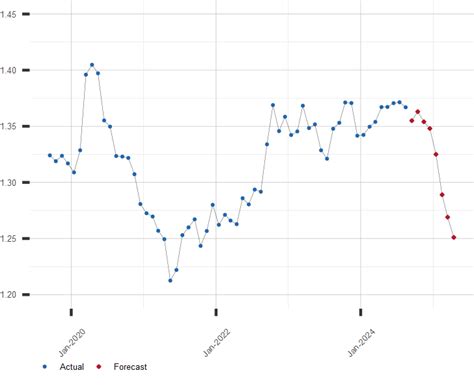
The Canadian dollar (CDN) and the United States dollar (USD) share a close and intricate relationship, driven by a myriad of economic and financial factors. The exchange rate between these two currencies has been in a constant state of flux, influenced by factors such as interest rate differentials, economic growth disparities, and geopolitical events.

Historical Perspective
Over the past century, the CDN-USD exchange rate has exhibited a cyclical pattern, oscillating between periods of appreciation and depreciation. In the early 1900s, the CDN traded at or above par with the USD, a reflection of Canada’s strong economic fundamentals and its close economic ties to the United States. However, during the Great Depression, the CDN depreciated sharply against the USD, falling to a low of $0.44 in 1933.
Post-World War II, the CDN regained strength, buoyed by Canada’s burgeoning oil and gas industry. In the 1960s, the CDN traded at a premium to the USD, reaching a peak of $1.08 in 1969. However, the oil crisis of the 1970s had a profound impact on the Canadian economy, leading to a devaluation of the CDN.
Key Economic Indicators
The following economic indicators play a crucial role in determining the CDN-USD exchange rate:
-
Interest Rates: Interest rate differentials between Canada and the United States heavily influence the exchange rate. When Canadian interest rates are higher than US interest rates, the CDN tends to appreciate as investors seek higher returns on Canadian assets.
-
Economic Growth: Differences in economic growth rates between Canada and the United States can impact the exchange rate. A stronger Canadian economy, characterized by robust GDP growth and low unemployment, typically leads to an appreciation of the CDN.
-
Trade Balance: The trade balance, which measures the difference between a country’s exports and imports, can also affect the exchange rate. A surplus in the trade balance tends to appreciate the currency of the exporting country.
-
Geopolitical Events: Major geopolitical events, such as wars or natural disasters, can have a significant impact on currency exchange rates. Uncertainty and risk aversion can lead to a flight to safety, resulting in a depreciation of currencies perceived as riskier.
Current Dynamics
In recent years, the CDN-USD exchange rate has been relatively stable, trading within a narrow range. However, there have been periods of volatility, particularly during times of economic uncertainty. The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, caused a sharp depreciation of the CDN in early 2020 due to concerns about its impact on the Canadian economy.
Currently, the CDN is trading at approximately $0.79 USD, reflecting a somewhat weaker Canadian dollar. This is primarily due to interest rate differentials, with the Bank of Canada (BOC) having adopted a more cautious approach to monetary policy compared to the Federal Reserve (Fed). The strength of the US economy, which has been recovering from the pandemic at a faster pace than Canada, has also contributed to the depreciation of the CDN.
Future Outlook
The future of the CDN-USD exchange rate is subject to a complex interplay of economic and geopolitical factors. Here are some key factors to consider:
-
Monetary Policy: The direction of the exchange rate will be heavily influenced by the monetary policies of the BOC and the Fed. If the BOC continues to maintain a more dovish stance than the Fed, the CDN could depreciate further.
-
Economic Growth: The relative strength of the Canadian and US economies will also be a key determinant of the exchange rate. A more robust economic growth outlook for Canada could lead to an appreciation of the CDN.
-
Global Economic Conditions: The overall global economic outlook will also play a role, with uncertainty and volatility potentially having a negative impact on the CDN.
-
Geopolitical Risks: Major geopolitical events, such as the ongoing war in Ukraine or tensions between the United States and China, could create volatility in the currency markets and impact the CDN-USD exchange rate.
Applications in Foreign Exchange
The CDN-USD exchange rate is a key consideration for businesses and individuals involved in cross-border transactions. By understanding the factors that influence the exchange rate and by actively monitoring market trends, it is possible to minimize foreign exchange risk and maximize the value of international payments.
Stochastics: Technical traders can use stochastic indicators to identify potential trading opportunities based on the relationship between the current CDN-USD exchange rate and its historical highs and lows.
Currency Pairs Trading: Advanced traders can engage in currency pairs trading, where they simultaneously buy and sell different currency pairs, such as CDN-USD and USD-JPY, to exploit exchange rate fluctuations.
Hedging Strategies: Businesses and individuals can use hedging strategies to protect themselves from adverse movements in the CDN-USD exchange rate. This can be achieved through the use of forward contracts, options, or currency swaps.
Table 1: Historical CDN-USD Exchange Rate
| Year | CDN-USD Exchange Rate |
|---|---|
| 1900 | 1.00 |
| 1933 | 0.44 |
| 1969 | 1.08 |
| 2000 | 0.67 |
| 2023 | 0.79 |
Table 2: Key Factors Influencing CDN-USD Exchange Rate
| Factor | Impact on CDN-USD Exchange Rate |
|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Higher Canadian interest rates lead to CDN appreciation |
| Economic Growth | Stronger Canadian economy leads to CDN appreciation |
| Trade Balance | Trade surplus leads to CDN appreciation |
| Geopolitical Events | Uncertainty and risk aversion lead to CDN depreciation |
Table 3: Tips for Managing Foreign Exchange Risk
| Tips | Impact |
|---|---|
| Understand the factors influencing the exchange rate | Avoid costly mistakes |
| Monitor market trends | Identify potential opportunities and risks |
| Use hedging strategies | Protect against adverse exchange rate movements |
| Consider forward contracts or currency swaps | Lock in exchange rates for future transactions |
Table 4: Pros and Cons of CDN-USD Exchange Rate Volatility
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Opportunity for speculation | Increased volatility can lead to losses |
| Potential for exchange rate gains | Can disrupt international trade and investment |
| Can hedge against currency risk | Can increase costs and complexity for businesses |