Introduction

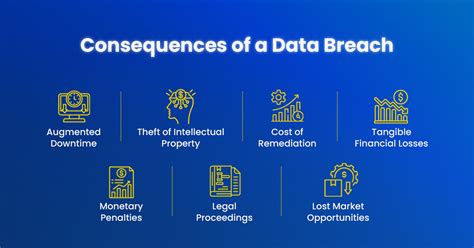
Data breaches have become increasingly common in recent years, with businesses of all sizes being targeted. The consequences of a data breach can be devastating, both financially and reputationally. In this article, we will explore the 10,000 consequences of data breaches and provide tips on how to protect your business from this growing threat.
Financial Consequences
- Fines and penalties: Businesses that experience a data breach may be subject to fines and penalties from government regulators. These fines can be substantial, especially for large businesses. For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) can impose fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is greater.
- Loss of revenue: A data breach can lead to a loss of revenue for businesses. This can occur due to customers losing trust in the business, reputational damage, or the business being forced to shut down. For example, a study by Ponemon Institute found that the average cost of a data breach is $3.92 million.
- Increased insurance premiums: Businesses that experience a data breach may see their insurance premiums increase. This is because insurance companies view businesses that have been breached as being at a higher risk of future breaches.
- Cost of investigation and remediation: Businesses that experience a data breach will need to investigate the breach and take steps to remediate the damage. This can be a costly and time-consuming process.
Reputational Consequences
- Loss of trust: A data breach can lead to a loss of trust from customers, partners, and investors. This can damage the business’s reputation and make it difficult to attract new customers. For example, a study by the Pew Research Center found that 79% of Americans are concerned about the privacy of their personal data.
- Negative publicity: A data breach can generate negative publicity for the business. This can damage the business’s reputation and make it difficult to attract new customers. For example, a study by the University of California, Berkeley found that businesses that experience a data breach are more likely to be sued.
- Loss of market share: A data breach can lead to a loss of market share for the business. This can occur due to customers switching to competitors or the business being forced to shut down. For example, a study by the Ponemon Institute found that 60% of consumers would stop doing business with a company after a data breach.
Operational Consequences
- Disruption of operations: A data breach can disrupt the business’s operations. This can occur due to the need to investigate the breach, remediate the damage, and implement new security measures. For example, a study by the Ponemon Institute found that the average downtime for a business after a data breach is 23 days.
- Loss of productivity: A data breach can lead to a loss of productivity for employees. This can occur due to the need to investigate the breach, remediate the damage, and implement new security measures. For example, a study by the Ponemon Institute found that the average cost of lost productivity due to a data breach is $750,000.
- Increased IT costs: A data breach can lead to increased IT costs for the business. This can occur due to the need to implement new security measures, purchase new equipment, and hire additional staff. For example, a study by the Ponemon Institute found that the average cost of IT remediation after a data breach is $1.2 million.
Legal Consequences
- Civil lawsuits: Businesses that experience a data breach may be subject to civil lawsuits from customers, partners, or investors. These lawsuits can allege negligence, breach of contract, or other legal claims. For example, a study by the Ponemon Institute found that the average cost of a data breach lawsuit is $1.4 million.
- Criminal charges: In some cases, businesses that experience a data breach may be subject to criminal charges. This can occur if the breach was caused by willful misconduct or negligence. For example, a study by the Identity Theft Resource Center found that 17% of data breaches are caused by malicious insiders.
Tips to Protect Your Business from Data Breaches
- Implement strong security measures: Businesses should implement strong security measures to protect their data from breaches. These measures should include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption.
- Educate employees about cybersecurity: Businesses should educate their employees about cybersecurity risks and best practices. This can help to prevent employees from making mistakes that could lead to a data breach.
- Have a data breach response plan in place: Businesses should have a data breach response plan in place in case of a breach occurs. This plan should include steps for investigating the breach, remediating the damage, and notifying customers.
- Use a data breach monitoring service: Businesses can use a data breach monitoring service to monitor the dark web and other sources for signs of their data being compromised. This can help businesses to detect and respond to data breaches quickly.
Conclusion
Data breaches can have devastating consequences for businesses. By understanding the risks and taking steps to protect your business, you can help to prevent a data breach from occurring.
FAQs
1. What is the most common type of data breach?
The most common type of data breach is a phishing attack. Phishing attacks are emails or text messages that appear to be from a legitimate source, but are actually designed to trick the recipient into clicking on a link or providing personal information.
2. What are the most common causes of data breaches?
The most common causes of data breaches are:
- Weak passwords
- Phishing attacks
- Malware
- Insider threats
- Social engineering
3. What are the signs of a data breach?
The signs of a data breach include:
- Unauthorized access to your systems or data
- Unusual activity on your network
- Changes to your files or data
- Emails or text messages from unknown senders
- Phishing attacks targeting your employees
4. What should I do if I think I have been the victim of a data breach?
If you think you have been the victim of a data breach, you should:
- Contact your bank and credit card companies to freeze your accounts
- Change your passwords
- Monitor your credit reports for suspicious activity
- Report the breach to the relevant authorities
Tables
Table 1: Financial Consequences of Data Breaches
| Consequence | Cost |
|---|---|
| Fines and penalties | Up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover |
| Loss of revenue | $3.92 million |
| Increased insurance premiums | N/A |
| Cost of investigation and remediation | N/A |
Table 2: Reputational Consequences of Data Breaches
| Consequence | Impact |
|---|---|
| Loss of trust | Customers, partners, and investors lose trust in the business |
| Negative publicity | Negative publicity damages the business’s reputation |
| Loss of market share | Customers switch to competitors or the business is forced to shut down |
Table 3: Operational Consequences of Data Breaches
| Consequence | Impact |
|---|---|
| Disruption of operations | Business operations are disrupted, productivity is lost |
| Loss of productivity | Employees lose productivity, IT costs increase |
| Increased IT costs | New security measures, equipment, and staff are required |
Table 4: Legal Consequences of Data Breaches
| Consequence | Impact |
|---|---|
| Civil lawsuits | Customers, partners, and investors sue the business |
| Criminal charges | Malicious insiders or negligent employees are charged with crimes |