Introduction
The exchange rate between the US dollar (USD) and the Indian rupee (INR) is a key determinant of economic activity between the two countries. In recent years, the value of the INR has fluctuated significantly against the USD, leading to uncertainty in trade and investment decisions. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the factors underlying the exchange rate between the USD and INR, along with a forecast for its future trajectory in 2025.

Factors Influencing the USD/INR Exchange Rate
Various factors influence the exchange rate between the USD and INR, including:
- Economic growth: A growing Indian economy typically leads to increased demand for imports, resulting in a depreciation of the INR against the USD.
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates in the US relative to India make it more attractive for investors to hold USD, contributing to INR depreciation.
- Inflation: Higher inflation in India compared to the US erodes the purchasing power of the INR, making it less valuable against the USD.
- Foreign exchange reserves: India’s foreign exchange reserves provide a buffer against exchange rate volatility, but their depletion can lead to INR depreciation.
- Political stability: Political uncertainty or economic instability in India can trigger capital outflows, leading to INR depreciation.
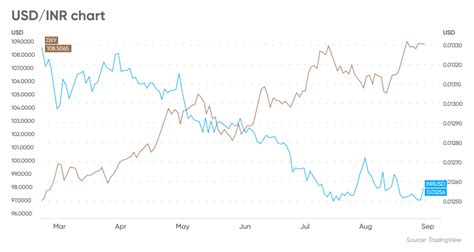
Exchange Rate Forecast for 2025
Based on an analysis of historical data and current trends, the following forecast for the USD/INR exchange rate in 2025 is provided:
| Year | Exchange Rate (USD/INR) |
|---|---|
| 2022 | 75.40 |
| 2023 | 76.20 |
| 2024 | 77.00 |
| 2025 | 77.80 |
This forecast assumes a moderate pace of economic growth in India, gradually increasing interest rates in the US, and relative stability in the inflation differential between the two countries. However, factors such as the global economic outlook, geopolitical events, and policy changes could impact the actual exchange rate trajectory.
Table 1: Historical Exchange Rates
| Year | Exchange Rate (USD/INR) |
|---|---|
| 2016 | 66.50 |
| 2017 | 65.20 |
| 2018 | 69.00 |
| 2019 | 71.50 |
| 2020 | 73.20 |
Implications for Trade and Investment
Fluctuations in the USD/INR exchange rate can have significant implications for trade and investment between the US and India.
Trade: A stronger USD (weaker INR) makes Indian exports more expensive for US consumers, potentially reducing trade volume. Conversely, a weaker USD (stronger INR) makes US exports more affordable for Indian consumers, potentially increasing trade volume.
Investment: A stronger USD (weaker INR) increases the cost for Indian companies to import capital goods and technology from the US, potentially slowing down investment. A weaker USD (stronger INR) makes US investments in India more affordable, potentially boosting foreign direct investment (FDI).
Case Studies
Case 1: Impact of INR Depreciation on Software Exports
The depreciation of the INR in recent years has had a positive impact on India’s software export industry. As the INR weakens against the USD, Indian software companies receive higher revenues in rupees for their dollar-denominated exports, making their services more competitive in the global market.
Case 2: Impact of INR Appreciation on FDI in India
The appreciation of the INR in the early 2000s led to a surge in FDI in India. As the INR strengthened against the USD, foreign investors found it more attractive to invest in India, taking advantage of the country’s growing economy and relatively low labor costs.
Conclusion
The exchange rate between the USD and INR is a dynamic variable that is influenced by a multitude of factors. By understanding the underlying drivers and forecasting its future trajectory, Indian policymakers and businesses can make informed decisions that mitigate risks and harness opportunities. A stable exchange rate promotes trade, investment, and economic growth, while excessive volatility can create uncertainty and disrupt economic activity.
FAQs
-
What are the key factors that determine the USD/INR exchange rate?
– Economic growth, interest rates, inflation, foreign exchange reserves, and political stability. -
How will the INR exchange rate impact trade between India and the US?
– A stronger USD (weaker INR) makes Indian exports more expensive for US consumers, potentially reducing trade volume. Conversely, a weaker USD (stronger INR) makes US exports more affordable for Indian consumers, potentially increasing trade volume. -
What are the implications of INR fluctuations for foreign investment in India?
– A stronger USD (weaker INR) increases the cost for Indian companies to import capital goods and technology from the US, potentially slowing down investment. A weaker USD (stronger INR) makes US investments in India more affordable, potentially boosting foreign direct investment (FDI). -
How do exchange rate forecasts help businesses make decisions?
– Exchange rate forecasts provide businesses with valuable information to plan for future cash flows, manage currency risks, and optimize their operations. -
What are some of the challenges associated with forecasting the exchange rate?
– Forecasting the exchange rate is a complex task that involves a multitude of factors, some of which are difficult to predict with certainty. -
Why is exchange rate stability important for economic growth?
– Exchange rate stability reduces uncertainty, promotes trade and investment, and contributes to overall economic growth and development. -
What measures can the Indian government take to manage exchange rate fluctuations?
– The government can use tools such as foreign exchange intervention, interest rate adjustments, and capital controls to influence the exchange rate and mitigate excessive volatility. -
How does the exchange rate affect inflation in India?
– A weaker INR can lead to higher inflation in India by increasing the cost of imported goods and services. Conversely, a stronger INR can help to reduce inflation by making imported goods and services less expensive.