Introduction
Copper, a versatile and essential metal, has played a pivotal role in human civilization for centuries. Its unique properties make it indispensable in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, electronics, and renewable energy. As a result, the price of copper has always been closely monitored by investors and analysts alike.

Historic Price Trends
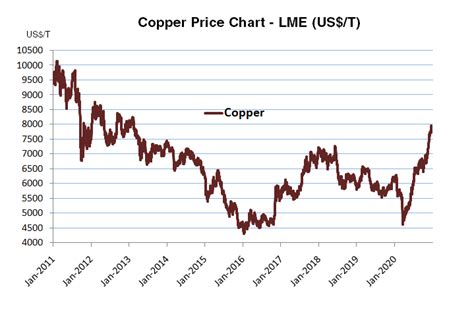
The price of copper has historically exhibited significant volatility, influenced by a multitude of economic, political, and technological factors. Over the past century, copper prices have experienced several bull and bear cycles, with some periods of sustained growth followed by sharp downturns.
| Period | Average Price per Ounce |
|---|---|
| 1900-1945 | $0.10-$0.25 |
| 1945-1970 | $0.25-$0.50 |
| 1970-1980 | $0.50-$1.00 |
| 1980-2000 | $1.00-$2.00 |
| 2000-present | $2.00-$10.00 |
Factors Influencing Copper Price
Demand and Supply: The interplay between global demand for copper and its supply from mining operations remains a primary driver of price fluctuations. Economic growth, technological advancements, and infrastructure development can all impact demand, while factors such as mining capacity, labor costs, and geopolitical events can affect supply.
Economic Conditions: The overall health of the global economy influences copper demand. Strong economic growth typically leads to increased consumption of copper, driving up prices. Conversely, recessions or economic slowdowns can result in lower demand and decreased prices.
Technological Advancements: The development of new technologies and applications for copper can stimulate demand. For instance, the rise of electric vehicles and renewable energy sources has increased the demand for copper in recent years.
Speculation and Investment: Copper is often traded as an investment asset, with investors speculating on future price movements. Speculative trading can contribute to price volatility, particularly in the short term.
Government Policies: Government actions, such as tax changes, mining regulations, and trade policies, can impact the cost of production and availability of copper, thereby influencing its price.
Future Projections to 2025
The long-term outlook for copper prices remains positive, driven by increasing demand from emerging economies and the transition to a more sustainable and electrified global economy. According to the International Copper Study Group (ICSG), global copper demand is projected to reach 50 million metric tons by 2025, a significant increase from the estimated 26 million metric tons consumed in 2022.
| Year | Projected Price per Ounce |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $4.50-$5.50 |
| 2024 | $5.50-$6.50 |
| 2025 | $6.50-$7.50 |
Strategies for Investors
Diversification: Incorporating copper into a diversified investment portfolio can mitigate risk and enhance returns. Investors can consider investing in copper-producing companies, futures contracts, or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track copper prices.
Long-Term Investment: Given the positive long-term outlook for copper, investors may consider adopting a long-term investment strategy. Historically, copper prices have exhibited resilience during periods of economic uncertainty and have outperformed many other commodities.
Hedging: Copper producers and consumers can employ hedging strategies to mitigate price volatility. Hedging involves entering into contracts that lock in future prices, protecting against potential losses or guaranteeing a minimum price.
Tips and Tricks
- Monitor global economic conditions, particularly in key copper-consuming regions such as China and India.
- Keep an eye on technological advancements that create new applications for copper.
- Consider the supply-demand balance and how factors like mining capacity and geopolitical events may impact supply.
- Understand the role of government policies and how they can influence copper production and trade.
- Consult with a financial advisor to develop an investment strategy that aligns with your individual risk tolerance and financial goals.
Pros and Cons of Investing in Copper
Pros:
- Diversification: Copper can provide diversification benefits and enhance overall portfolio returns.
- Long-term Growth Potential: Copper demand is expected to continue growing over the long term, driven by economic development and technological advancements.
- Government Support: Governments in many copper-producing countries provide support to the industry, promoting stability and growth.
- Finite Resource: Copper is a finite resource, so its value is less likely to be eroded by inflation over time.
Cons:
- Price Volatility: Copper prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate significantly in the short term.
- Economic Downturns: Economic recessions or slowdowns can negatively impact copper demand and prices.
- Political Risk: Copper mining operations are often located in countries with political instability, which can pose risks to supply chains.
- Environmental Concerns: Copper mining can have environmental implications, so investors may need to consider sustainability factors.
FAQs
- Why is copper so valuable? Copper is a highly conductive and malleable metal, making it ideal for use in electrical and thermal applications. Its resistance to corrosion is another reason for its value.
- What factors can affect the supply of copper? The supply of copper can be influenced by factors such as mining capacity, labor strikes, and geopolitical events that disrupt production.
- What is the difference between copper spot price and futures price? The spot price reflects the current market price for copper, while the futures price is the price at which copper is contracted to be delivered at a future date.
- How is copper used in renewable energy? Copper is extensively used in solar panels, wind turbines, and electric vehicle motors, all of which are essential components of a sustainable energy future.
- What are some creative applications for copper? Researchers are exploring the use of copper in antibacterial surfaces, flexible electronics, and even as a catalyst in chemical reactions.
- How can I invest in copper? You can invest in copper by purchasing stocks of copper-producing companies, trading futures contracts, or investing in ETFs that track copper prices.