Start your investment journey now and reach your financial goals with our powerful calculator.

Dollar Cost Averaging Calculator
Input:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Starting amount | $10,000 |
| Monthly contribution | $500 |
| Investment duration | 10 years |
| Annualized return rate | 7% |
Output:
| Year | Total Invested | Account Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $6,000 | $6,391 |
| 2 | $12,000 | $13,275 |
| 3 | $18,000 | $20,736 |
| 4 | $24,000 | $28,875 |
| 5 | $30,000 | $37,804 |
| 6 | $36,000 | $47,634 |
| 7 | $42,000 | $58,485 |
| 8 | $48,000 | $70,490 |
| 9 | $54,000 | $83,774 |
| 10 | $60,000 | $98,492 |
Total Earnings: $38,492
Understanding Dollar Cost Averaging
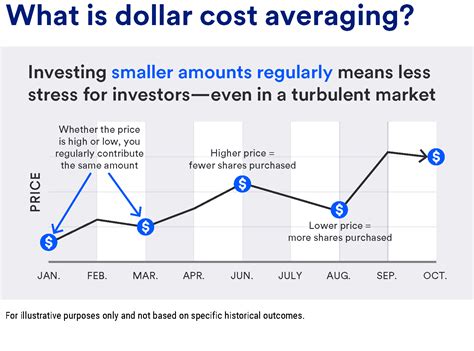
Dollar cost averaging (DCA) is an investment strategy that involves making regular, fixed-dollar investments in a particular asset over a period of time. This approach helps investors reduce the impact of market volatility on their investments.
How DCA Works
When you invest using DCA, you purchase the same dollar amount of an asset at regular intervals, regardless of its price. This means that you will buy more shares when the price is low and fewer shares when the price is high. Over time, this strategy averages out the cost of your investments and reduces the risk of significant losses.
Benefits of DCA
- Reduced Risk: DCA helps mitigate the impact of market fluctuations by distributing your investments over time.
- Simplified Investing: This strategy requires less time and effort than trying to time the market.
- Potential for Growth: DCA can help you accumulate wealth over the long term by taking advantage of compound interest.
Effective Strategies for DCA
Start Early and Invest Consistently: The sooner you start investing and the more consistently you contribute, the greater the potential for growth.
Set Realistic Goals: Consider your financial situation and risk tolerance when determining how much to invest.
Choose a Low-Cost Investment: Opt for investments with low expense ratios, such as index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Rebalance Your Portfolio: Regularly review your portfolio and adjust the allocation of your investments to maintain your desired risk level.
Tips and Tricks for DCA
- Automate Your Investments: Set up automatic transfers from your bank account to your investment account on a regular basis.
- Use Round-Up Apps: Link your debit or credit card to an app that rounds up your purchases and invests the extra funds.
- Consider Fractional Shares: Some platforms allow you to purchase fractional shares, making it possible to invest smaller amounts in your target assets.
Pros and Cons of DCA
Pros:
- Reduced risk
- Simplified investing
- Potential for growth
Cons:
- Less potential upside than investing a lump sum
- Can be slow to accumulate wealth
- May not be suitable for short-term investments
FAQs
-
What is the best asset class for DCA?
– Equities, bonds, or a combination of both can be suitable depending on your risk tolerance and investment goals. -
How often should I invest using DCA?
– Monthly or quarterly intervals are common. -
Is DCA only suitable for small amounts of money?
– No, you can invest any amount using DCA. -
Can I stop investing using DCA at any time?
– Yes, you can stop or pause your investments at any time. -
What is the best way to choose an investment for DCA?
– Consider your risk tolerance, investment goals, and the expense ratios of different investments. -
Is DCA a guaranteed way to make money?
– No, all investments involve some level of risk. However, DCA can help reduce the impact of market fluctuations. -
Can I use DCA to invest in individual stocks?
– Yes, but it is important to diversify your investments to reduce risk. -
What is a creative application of DCA?
– “Smart DCA” involves automatically increasing your investment amount over time based on factors such as market volatility or your income.