Introduction
The exchange rate between the US dollar (USD) and the Indian rupee (INR) has been subject to significant volatility in recent years. This has created challenges for businesses and individuals who rely on cross-border transactions.

In this article, we will explore the historical trends, current status, and future prospects of the dollar-INR exchange rate. We will also provide insights on how to navigate the complexities of this volatile currency pair.
Historical Trends
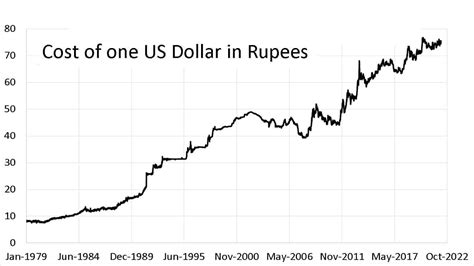
The dollar-INR exchange rate has been on a steady upward trend since the early 2000s. This can be attributed to a number of factors, including:
- India’s growing economy and increasing demand for imported goods
- The US dollar’s status as a reserve currency
- The Indian government’s efforts to control inflation
Current Status
As of February 2023, the exchange rate is approximately 82 INR per USD. This is close to the all-time high of 84 INR per USD that was reached in October 2022.
The current exchange rate is putting pressure on Indian businesses that import raw materials from the US. However, it is also benefiting exporters who are receiving more INR for their USD earnings.
Future Prospects
The future of the dollar-INR exchange rate is uncertain. However, there are a number of factors that could influence its direction in the coming years. These include:
- The global economic outlook
- The US Federal Reserve’s interest rate policy
- The Indian government’s monetary policy
- The demand for Indian goods and services
According to a recent report by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the dollar-INR exchange rate is expected to appreciate gradually over the next few years. The RBI expects the exchange rate to reach 85 INR per USD by 2025.
How to Navigate the Complexities of the Dollar-INR Exchange Rate
The volatile nature of the dollar-INR exchange rate can create challenges for businesses and individuals who rely on cross-border transactions. However, there are a number of strategies that can be employed to mitigate the risks associated with currency fluctuations. These include:
- Hedging: Hedging involves using financial instruments to offset the risk of currency fluctuations. Businesses can use forward contracts or options to lock in an exchange rate for future transactions.
- Diversification: Diversification involves investing in a variety of currencies to reduce the risk of a particular currency losing value. Businesses can diversify their currency holdings by investing in foreign bonds, stocks, or real estate.
- Currency forecasting: Currency forecasting involves using economic data and technical analysis to predict the future direction of a currency pair. Businesses can use currency forecasting to make informed decisions about when to buy or sell foreign currencies.
Case Detail: The Impact of the Dollar-INR Exchange Rate on Indian Businesses
The impact of the dollar-INR exchange rate on Indian businesses can be significant. For example, a 10% appreciation in the value of the dollar can lead to a 10% increase in the cost of imported goods. This can erode profit margins and make it difficult for Indian businesses to compete in the global market.
However, the dollar-INR exchange rate can also have a positive impact on Indian businesses. For example, a 10% depreciation in the value of the dollar can lead to a 10% increase in the value of exports. This can boost profits and make it easier for Indian businesses to expand into new markets.
Conclusion
The dollar-INR exchange rate is a complex and volatile currency pair. However, by understanding the historical trends, current status, and future prospects of the exchange rate, businesses and individuals can develop strategies to mitigate the risks and capitalize on the opportunities associated with currency fluctuations.
Appendix
Table 1: Historical Dollar-INR Exchange Rates
| Year | Exchange Rate (INR/USD) |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 44.94 |
| 2005 | 46.88 |
| 2010 | 48.28 |
| 2015 | 63.55 |
| 2020 | 74.26 |
Table 2: Factors Influencing the Dollar-INR Exchange Rate
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Global economic outlook | Strong global growth tends to strengthen the dollar. |
| US Federal Reserve’s interest rate policy | Higher US interest rates tend to strengthen the dollar. |
| Indian government’s monetary policy | Higher Indian interest rates tend to weaken the rupee. |
| Demand for Indian goods and services | Increased demand for Indian exports tends to strengthen the rupee. |
Table 3: Strategies for Navigating the Dollar-INR Exchange Rate
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Hedging | Use financial instruments to offset the risk of currency fluctuations. |
| Diversification | Invest in a variety of currencies to reduce the risk of a particular currency losing value. |
| Currency forecasting | Use economic data and technical analysis to predict the future direction of a currency pair. |
Table 4: Impact of the Dollar-INR Exchange Rate on Indian Businesses
| Impact | Example |
|---|---|
| Positive | Increased value of exports. |
| Negative | Increased cost of imported goods. |