Understanding the Basics
An exchange rate is the value of one currency in terms of another. In the case of the US dollar (USD) and Canadian dollar (CAD), the exchange rate determines how many CAD you can buy with one USD. The exchange rate is constantly fluctuating due to various economic factors, such as interest rates, economic growth, and inflation.

Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
Numerous factors influence the exchange rate between the USD and CAD:
- Economic growth: A stronger economy tends to have a higher currency value.
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency.
- Inflation: Inflation erodes the value of a currency over time.
- Fiscal policy: Government spending and taxation can affect the currency’s value.
- Monetary policy: Central banks’ actions, such as setting interest rates and buying/selling currencies, can influence exchange rates.
Historical Trends
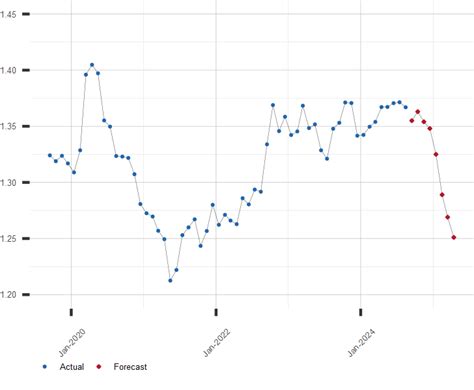
Historically, the USD has been stronger than the CAD. Over the past decade, the exchange rate has ranged from roughly 0.75 CAD to 1.40 CAD per USD. The average exchange rate in 2022 was 1.25 CAD per USD.
Forecasting the Future
Predicting the future exchange rate is challenging due to the numerous factors involved. However, analysts expect the USD to remain stronger than the CAD in the coming years.
Implications for Businesses and Individuals
The exchange rate affects businesses and individuals in various ways:
- Importers and Exporters: A weaker CAD makes it more expensive for Canadian businesses to import goods from the US, while a stronger CAD makes it cheaper for US businesses to export goods to Canada.
- Travelers: A weaker CAD makes it more expensive for Canadians to travel to the US, while a stronger CAD makes it cheaper for Americans to visit Canada.
- Investors: Exchange rate fluctuations can impact the value of investments in foreign markets.
Opportunities and Challenges
The fluctuating exchange rate presents both opportunities and challenges:
- Opportunities: Businesses can take advantage of favorable exchange rates to increase profits on imports or exports.
- Challenges: Businesses need to manage the risks associated with exchange rate volatility, which can impact their margins and profitability.
Effective Strategies
To mitigate the risks and maximize the opportunities associated with exchange rate fluctuations, consider these strategies:
- Hedge against currency fluctuations: Use financial instruments such as options or forward contracts to lock in an exchange rate.
- Diversify your investments: Invest in assets denominated in multiple currencies to reduce exposure to exchange rate risk.
- Monitor market conditions: Stay informed about economic factors and geopolitical events that may impact exchange rates.
Step-by-Step Approach to Understanding Exchange Rates
- Identify the primary factors influencing exchange rates.
- Monitor historical trends and analyze patterns in exchange rates.
- Forecast future exchange rates using available data and forecasts.
- assess the implications of exchange rate fluctuations on your business or personal finances.
- Develop and implement effective strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
Conclusion
The exchange rate between the USD and CAD is a complex and dynamic phenomenon influenced by a multitude of economic factors. Understanding the factors, historical trends, and future forecasts can help businesses and individuals navigate the challenges and seize the opportunities presented by exchange rate fluctuations. By implementing appropriate strategies, you can mitigate risks, optimize profits, and make informed decisions in today’s globalized economy.
Tables
Table 1: Historical Exchange Rates (USD/CAD)
| Year | Average Exchange Rate |
|---|---|
| 2012 | 1.01 |
| 2013 | 1.04 |
| 2014 | 1.09 |
| 2015 | 1.25 |
| 2016 | 1.33 |
| 2017 | 1.28 |
| 2018 | 1.30 |
| 2019 | 1.33 |
| 2020 | 1.32 |
| 2021 | 1.27 |
| 2022 | 1.25 |
Table 2: Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Economic Growth | A stronger economy leads to a higher currency value. |
| Interest Rates | Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency. |
| Inflation | Inflation erodes the value of a currency over time. |
| Fiscal Policy | Government spending and taxation can affect the currency’s value. |
| Monetary Policy | Central banks’ actions, such as setting interest rates and buying/selling currencies, can influence exchange rates. |
Table 3: Exchange Rate Implications
| Group | Impact |
|---|---|
| Importers and Exporters | A weaker CAD makes imports more expensive, while a stronger CAD reduces their cost. |
| Travelers | A weaker CAD makes travel more expensive, while a stronger CAD makes it cheaper. |
| Investors | Exchange rate fluctuations can impact the value of investments in foreign markets. |
Table 4: Exchange Rate Strategies
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Hedge against fluctuations | Use options or forward contracts to lock in an exchange rate. |
| Diversify investments | Invest in assets denominated in multiple currencies to reduce exchange rate risk. |
| Monitor market conditions | Stay informed about economic factors and geopolitical events that may impact exchange rates. |