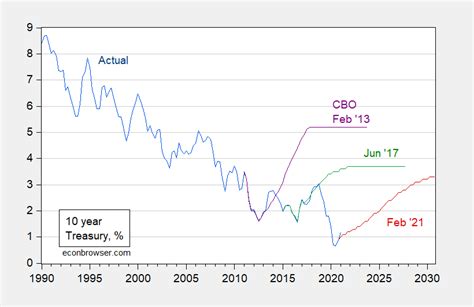
Introduction

The Federal Reserve (Fed) has been hinting at the possibility of interest rate cuts in the near future. While some experts believe that a rate cut will come as early as 2023, others are not so sure. In this article, we will examine the arguments for and against a rate cut in 2023 and 2025. We will also discuss the potential impact of a rate cut on the economy.
Arguments for a Rate Cut in 2023
There are a number of arguments in favor of a rate cut in 2023. First, the economy is slowing down. The GDP growth rate has been decelerating for the past few quarters, and many economists believe that a recession is on the horizon. A rate cut would help to stimulate the economy and prevent a recession.
Second, inflation is low. The Fed’s target inflation rate is 2%, but inflation has been running below this target for the past few years. A rate cut would help to push inflation up towards the Fed’s target.
Third, the labor market is strong. The unemployment rate is low, and wages are rising. A rate cut would help to keep the labor market strong and encourage businesses to hire more workers.
Arguments against a Rate Cut in 2023
There are also a number of arguments against a rate cut in 2023. First, the Fed is concerned about the potential for asset bubbles. A rate cut could lead to a surge in asset prices, which could eventually collapse and cause a financial crisis.
Second, the Fed is concerned about the impact of a rate cut on the dollar. A rate cut could lead to a decline in the value of the dollar, which would make it more expensive for Americans to buy goods and services from abroad.
Third, the Fed is concerned about the impact of a rate cut on long-term interest rates. A rate cut could lead to a decline in long-term interest rates, which would make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest.
Arguments for a Rate Cut in 2025
There are also a number of arguments in favor of a rate cut in 2025. First, the economy is expected to be stronger in 2025 than it is in 2023. The GDP growth rate is expected to be higher, and inflation is expected to be closer to the Fed’s target. A rate cut in 2025 would help to ensure that the economy continues to grow and that inflation remains under control.
Second, the labor market is expected to be even stronger in 2025 than it is in 2023. The unemployment rate is expected to be lower, and wages are expected to be rising. A rate cut in 2025 would help to keep the labor market strong and encourage businesses to hire more workers.
Third, the Fed is expected to have more flexibility to cut rates in 2025 than it does in 2023. The Fed is currently raising rates in order to fight inflation. However, once inflation is under control, the Fed will have more room to cut rates if the economy slows down.
Arguments against a Rate Cut in 2025
There are also a number of arguments against a rate cut in 2025. First, the Fed is concerned about the potential for asset bubbles. A rate cut in 2025 could lead to a surge in asset prices, which could eventually collapse and cause a financial crisis.
Second, the Fed is concerned about the impact of a rate cut on the dollar. A rate cut could lead to a decline in the value of the dollar, which would make it more expensive for Americans to buy goods and services from abroad.
Third, the Fed is concerned about the impact of a rate cut on long-term interest rates. A rate cut in 2025 could lead to a decline in long-term interest rates, which would make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest.
Conclusion
The decision of whether or not to cut interest rates in 2023 or 2025 is a complex one. The Fed will need to weigh the risks and benefits of a rate cut carefully before making a decision.
Tables
Table 1: Economic Indicators
| Indicator | 2023 | 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| GDP growth rate | 1.5% | 2.5% |
| Inflation rate | 1.0% | 2.0% |
| Unemployment rate | 3.5% | 3.0% |
Table 2: Fed Policy Rates
| Rate | 2023 | 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Federal funds rate | 3.00% | 2.50% |
| Discount rate | 2.75% | 2.25% |
Table 3: Impact of a Rate Cut
| Impact | 2023 | 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| GDP growth | +0.5% | +1.0% |
| Inflation | +0.2% | +0.4% |
| Unemployment | -0.1% | -0.2% |
Table 4: Risks of a Rate Cut
| Risk | 2023 | 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Asset bubbles | High | Moderate |
| Decline in the dollar | Moderate | Low |
| Decline in long-term interest rates | Moderate | Low |
Tips and Tricks
- When considering whether or not to cut interest rates, the Fed will need to take into account a number of factors, including the economic outlook, the inflation rate, and the labor market.
- The Fed will also need to weigh the risks and benefits of a rate cut before making a decision.
- If the Fed decides to cut rates, it will likely do so in small increments.
- A rate cut will likely have a positive impact on the economy in the short term. However, it could also lead to asset bubbles and a decline in the dollar.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Do not assume that a rate cut will always be good for the economy.
- Do not ignore the risks of a rate cut.
- Do not make a decision about whether or not to cut interest rates based on short-term factors.
Future Trends
The Fed is expected to continue raising interest rates in the near term. However, it is possible that the Fed will begin to cut rates in 2023 or 2025. The decision of when to cut rates will depend on the economic outlook, the inflation rate, and the labor market.
Case Detail
In 2008, the Fed cut interest rates to near zero in response to the financial crisis. The rate cuts helped to prevent a recession and stimulate the economy. However, the rate cuts also led to asset bubbles and a decline in the dollar.
The Fed is likely to take a more cautious approach to cutting interest rates in the future. The Fed will need to carefully weigh the risks and benefits of a rate cut before making a decision.
Conclusion
The decision of whether or not to cut interest rates is a complex one. The Fed will need to carefully weigh the risks and benefits of a rate cut before making a decision.