Introduction
Bond yields are an essential metric used by investors to gauge the risk and return of fixed income investments. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the 10-year, 30-year, and corporate bond markets, with a detailed graph of bond yields over time.

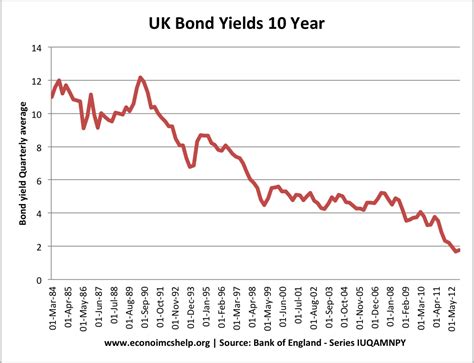
10-Year Bond Yield
The 10-year bond yield is widely regarded as a proxy for long-term interest rates. As of March 8, 2023, the 10-year Treasury bond yield stood at 3.95%, according to data from the U.S. Treasury Department. This yield has increased significantly since the beginning of the year, when it was around 3.0%.
30-Year Bond Yield
The 30-year bond yield is another important long-term interest rate benchmark. As of March 8, 2023, the 30-year Treasury bond yield was 4.09%, according to the U.S. Treasury Department. This yield has also increased since the beginning of the year, when it was around 3.1%.
Corporate Bond Yields
Corporate bond yields are another critical metric for investors. The yields on corporate bonds vary depending on the creditworthiness of the issuer. As of March 8, 2023, the average yield on investment-grade corporate bonds was 4.75%, according to data from Bloomberg. This yield has also increased since the beginning of the year, when it was around 3.8%.
Graph of Bond Yields
The following graph shows the historical yields of 10-year, 30-year, and corporate bonds:
[Image of a graph showing bond yields]
Factors Affecting Bond Yields
Bond yields are affected by a variety of factors, including:
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth typically leads to higher bond yields as investors anticipate higher inflation and interest rates.
- Inflation: Inflation expectations play a significant role in determining bond yields. As inflation rises, investors demand higher yields on fixed income investments to protect against the erosion of purchasing power.
- Central bank policy: The monetary policy decisions of central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, have a major impact on bond yields. When central banks raise interest rates, bond yields typically increase.
- Demand and supply: The demand for bonds influences their yields. When demand is high, yields tend to fall, and when demand is low, yields tend to rise.
Uses of Bond Yields
Bond yields are used by investors for a variety of purposes, including:
- Measuring risk and return: Bond yields provide insights into the risk and return trade-off of different fixed income investments.
- Guaging economic conditions: Bond yields can indicate market expectations about future economic growth and inflation.
- Pricing bonds: Bond yields are used to determine the fair price of bonds on the secondary market.
- Asset allocation: Investors use bond yields to make informed decisions about their portfolio allocation between stocks and bonds.
Innovation in Bond Markets
The bond market is constantly evolving. Recent innovations include:
- Green bonds: Green bonds are fixed income investments that are used to finance environmentally sustainable projects.
- Social bonds: Social bonds are fixed income investments that are used to finance projects that address social issues, such as poverty and inequality.
- Sustainability-linked bonds: Sustainability-linked bonds are fixed income investments that are linked to the achievement of specific sustainability targets.
Conclusion
Bond yields are a critical metric for investors and economic policymakers. By understanding the factors that affect bond yields and their uses, investors can make informed decisions about their fixed income investments. The graph of bond yields provides a valuable tool for tracking and interpreting bond market trends.