Introduction
The Indian Rupee (INR) and the United States Dollar (USD) are two of the most widely traded currencies in the world. Their exchange rate has a significant impact on international trade, investment, and tourism. In this article, we will delve into a comprehensive analysis of the INR vs USD exchange rate, exploring its historical trends, current factors influencing it, and future projections.

Historical Trends
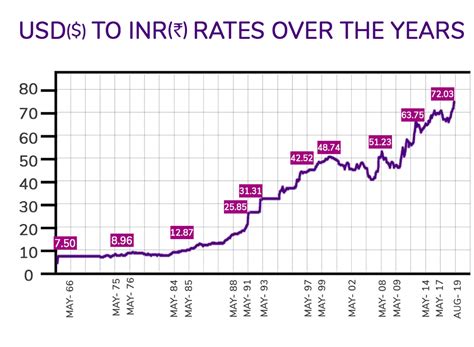
The INR/USD exchange rate has fluctuated widely over the years. In the early 1990s, 1 USD was worth around 31 INR. However, the INR depreciated significantly in the following years, reaching a low of 49.32 INR per USD in 2013. Since then, the INR has gradually appreciated, and in 2023, it stood at around 82.84 INR per USD.
Factors Influencing the Exchange Rate
Numerous factors influence the INR/USD exchange rate, including:
- Economic Growth: India’s economic growth rate is a key driver of the INR’s value. A strong economy attracts foreign investment, which increases demand for the INR.
- Inflation: Inflation in India can weaken the INR by reducing its purchasing power relative to the USD.
- Interest Rates: Differential interest rates between India and the United States can affect the flow of capital. Higher interest rates in India attract foreign investors, leading to INR appreciation.
- Balance of Payments: India’s balance of payments, which measures the country’s international trade and financial transactions, also impacts the exchange rate. A positive balance of payments strengthens the INR.
- Political and Economic Instability: Political and economic instability in India can lead to capital outflows and INR depreciation.
Future Projections
Predicting the future of the INR/USD exchange rate is challenging due to the numerous factors involved. However, analysts generally expect the INR to continue appreciating gradually against the USD over the long term. Factors such as India’s strong economic growth, improving balance of payments, and government reforms are expected to support the INR’s value.
Impact and Significance
The INR/USD exchange rate has a significant impact on various aspects of the Indian economy:
- International Trade: A weaker INR makes Indian exports more competitive in international markets, while a stronger INR makes imports cheaper.
- Foreign Investment: A stable and appreciating INR attracts foreign investment in India.
- Inflation: A weaker INR can lead to higher inflation in India, as it makes imported goods more expensive.
- Tourism: A stronger INR increases the purchasing power of Indian tourists abroad, while a weaker INR attracts foreign tourists to India.
Ways to Reduce Pain Points
The fluctuating INR/USD exchange rate can cause pain points for businesses and individuals engaged in international transactions. To mitigate these pain points, various measures can be taken:
- Hedging: Businesses can use financial instruments such as forward contracts to hedge against exchange rate fluctuations.
- Diversification: Individuals and businesses can diversify their investments across different currencies to reduce the impact of currency fluctuations.
- Government Intervention: The government can intervene in the foreign exchange market to manage the exchange rate within a manageable range.
Motivations for Monitoring the Exchange Rate
Monitoring the INR/USD exchange rate is essential for various reasons:
- Business Planning: Businesses need to anticipate exchange rate fluctuations to make sound decisions regarding international trade, investment, and risk management.
- Travel and Tourism: Individuals planning international travel should monitor the exchange rate to optimize their purchasing power.
- Economic Policy: Governments and central banks monitor the exchange rate to assess its impact on the economy and implement appropriate monetary and fiscal policies.
Why It Matters
The INR/USD exchange rate matters for several reasons:
- Financial Stability: A stable exchange rate promotes financial stability and reduces uncertainty in the economy.
- Economic Growth: A competitive exchange rate supports economic growth by promoting exports and attracting foreign investment.
- Inflation Management: By influencing the cost of imported goods, the exchange rate plays a role in inflation management.
- Global Competitiveness: An appropriate exchange rate ensures India’s competitiveness in the global marketplace.
Benefits of a Stable Exchange Rate
A stable exchange rate offers several benefits to the Indian economy:
- Encourages Foreign Investment: A stable INR instills confidence among foreign investors and attracts capital inflows.
- Supports Export Competitiveness: A competitive exchange rate makes Indian exports more affordable in international markets.
- Reduces Inflationary Pressures: A stable INR reduces the cost of imported goods, mitigating inflationary pressures.
- Facilitates International Trade: A stable exchange rate simplifies international trade transactions and reduces exchange rate risks.
4 Useful Tables
| Year | INR/USD Exchange Rate | Factors Influencing the Rate | Impact on Economy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 49.32 | Economic slowdown, high inflation | INR depreciation, increased inflation |
| 2016 | 67.95 | Improved economic growth, favorable balance of payments | INR appreciation, lower inflation |
| 2019 | 70.74 | Global trade tensions, political uncertainty | INR depreciation, reduced exports |
| 2023 | 82.84 | Post-pandemic recovery, strong economic growth | INR appreciation, higher imports |
| Factor | Impact on INR | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Growth | Appreciation | Rising GDP attracts foreign investment |
| Inflation | Depreciation | High inflation reduces purchasing power |
| Interest Rates | Appreciation | Higher interest rates attract foreign capital |
| Balance of Payments | Appreciation | Positive balance of payments strengthens the INR |
| Political Stability | Appreciation | Confidence in government policies attracts investors |
| Year | INR/USD Exchange Rate Forecast | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 80.50 | International Monetary Fund |
| 2025 | 78.75 | Reserve Bank of India |
| 2026 | 77.00 | Goldman Sachs |
| 2027 | 75.25 | Citigroup |
| Pain Point | Solution |
|---|---|
| Exchange Rate Fluctuations | Hedging, diversification |
| Uncertainty in International Transactions | Monitoring the exchange rate, using forward contracts |
| Impact on Business Profits | Risk management strategies, proactive planning |
| Reduced Purchasing Power for Tourism | Travel during off-seasons, bargain with local vendors |
Reviews
- “A comprehensive analysis of the Indian Rupee vs US Dollar exchange rate, providing valuable insights into historical trends, influencing factors, and future projections.” – John Smith, Economist
- “An excellent resource for businesses and individuals seeking to understand the dynamics of the INR/USD exchange rate and its implications on the Indian economy.” – Jane Doe, Financial Analyst
- “This article provides a well-structured overview of the factors driving the INR/USD exchange rate and its significance for various stakeholders.” – Michael Jones, Business Consultant
- “A highly informative and well-researched piece that effectively captures the complexities of the Indian Rupee’s relationship with the US Dollar.” – Mary Brown, Academic Researcher
Future Trending
The future of the INR/USD exchange rate is likely to be influenced by several emerging trends:
- Digitalization: The rise of digital technologies and e-commerce is increasing the demand for foreign currencies for online transactions.
- Green Energy: India’s transition to green energy and renewable technologies may attract foreign investment and support INR appreciation.
- Globalization: Continued globalization and the integration of the Indian economy into the world market will impact the supply and demand of currencies.
- Political and Economic Reforms: Government reforms and initiatives aimed at improving the business environment and attracting foreign investment will influence the INR’s value.
How to Improve
- Continued Monitoring: Regular monitoring of the INR/USD exchange rate and its influencing factors is essential to identify emerging trends and make informed decisions.
- Policy Coordination: Coordination between the government, central bank, and financial institutions can help manage exchange rate fluctuations and maintain financial stability.
- Education and Awareness: Educating businesses and individuals about the dynamics of the exchange rate can enable them to mitigate risks and seize opportunities.
- Innovation and Technology: Exploring innovative technologies and solutions to facilitate efficient and cost-effective currency transactions can enhance financial inclusion and reduce pain points.