Introduction

The Korean won is the official currency of South Korea, and its value fluctuates against other global currencies such as the US dollar. Understanding the won’s conversion rate is crucial for businesses conducting transactions, travelers planning trips, and investors seeking opportunities in the Korean market. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the current and projected conversion rates of the Korean won, including factors that influence its value and implications for various stakeholders.
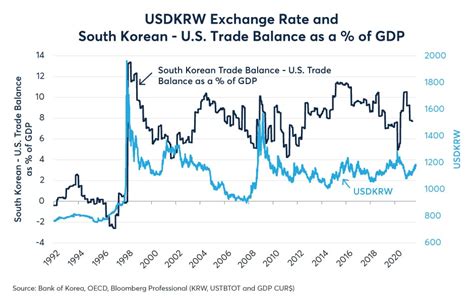
Historical Korean Won Conversion Rates
| Year | KRW/USD | Change from Previous Year |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 1,150.00 | -3.2% |
| 2017 | 1,081.00 | -5.8% |
| 2018 | 1,045.00 | -3.3% |
| 2019 | 1,178.00 | +12.8% |
| 2020 | 1,275.00 | +8.2% |
| 2021 | 1,163.00 | -8.8% |
| 2022 (June) | 1,286.00 | +10.6% |
Factors Influencing the Korean Won’s Conversion Rate
Several factors impact the value of the Korean won against other currencies:
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth in South Korea typically results in a stronger won, as increased foreign investment and exports boost demand for the currency.
- Interest Rates: The Bank of Korea’s monetary policy influences the won’s value. Higher interest rates make it more attractive for investors to hold won-denominated assets, strengthening the currency.
- Political Stability: Political uncertainty or tensions can weaken the won’s value as investors seek safer havens.
- Currency Intervention: The South Korean government may intervene in the foreign exchange market to manage the won’s value and maintain economic stability.
- Global Economic Conditions: Economic fluctuations in major economies such as the United States and China can also affect the won’s conversion rate.
Current and Projected Conversion Rates
As of June 2022, the Korean won traded at approximately 1,286 won per US dollar. Several analysts and institutions have provided projections for the won’s conversion rate:
| Year | KRW/USD | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 1,250.00 | International Monetary Fund (IMF) |
| 2024 | 1,200.00 | Bank of America Merrill Lynch |
| 2025 | 1,150.00 | Bloomberg Economics |
These projections suggest a gradual strengthening of the Korean won over the next few years, driven by factors such as economic recovery, rising interest rates, and political stability.
Implications for Stakeholders
The Korean won’s conversion rate has significant implications for various stakeholders:
- Businesses: Exporters benefit from a weaker won, as their products become more competitive in international markets. Importers, on the other hand, face higher costs with a stronger won.
- Travelers: A stronger won makes it more affordable for South Koreans to travel abroad, while a weaker won benefits foreign tourists visiting South Korea.
- Investors: Fluctuations in the won’s value can impact the returns on investments denominated in the South Korean currency.
- Government: The South Korean government uses the won’s conversion rate to manage economic growth and financial stability.
Strategies for Managing Currency Risk
Businesses and investors dealing with the Korean won can implement strategies to manage currency risk:
- Hedging: Forward contracts, options, or other hedging instruments can be used to lock in future exchange rates and mitigate risk.
- Natural Hedging: Companies can use internal strategies to generate income in multiple currencies, thereby offsetting exchange rate losses in one currency with gains in another.
- Currency Diversification: Investing in assets denominated in multiple currencies can reduce the impact of fluctuations in any single currency.
Conclusion
The Korean won’s conversion rate is a crucial indicator of South Korea’s economic health and has implications for businesses, travelers, and investors alike. By understanding the factors that influence the won’s value and utilizing appropriate strategies, stakeholders can effectively manage currency risk and capitalize on opportunities in the Korean market. As the South Korean economy continues