Introduction
In the ever-evolving realm of blockchain technology, two distinct consensus mechanisms – Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) – have emerged as formidable contenders for establishing network security and transaction validation. Each mechanism boasts unique characteristics and advantages, driving the debate over which approach will ultimately reign supreme in 2025 and beyond.

Proof of Work (PoW)
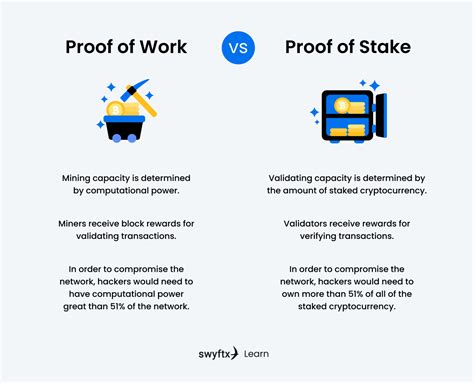
PoW is a time-tested consensus mechanism that has been employed by pioneering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. It relies on computational power to solve complex mathematical problems, with the first miner to find the solution rewarded with the next block of transactions. This process is inherently energy-intensive, requiring vast amounts of electricity to maintain network security.
Advantages:
- High level of security due to computational complexity
- Decentralised nature, as anyone with the necessary resources can participate
- Proven track record with established cryptocurrencies
Disadvantages:
- High energy consumption, contributing to environmental concerns
- Slow block processing times, leading to higher transaction fees
- Susceptible to 51% attacks if a single entity gains control of a majority of the network’s computational power
Proof of Stake (PoS)
PoS, a more recent consensus mechanism, leverages a different approach. Instead of relying on computational power, it uses the concept of staking. Here, validators are randomly selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold (stake) and are responsible for validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain. The more cryptocurrency a validator stakes, the higher their chances of being chosen.
Advantages:
- Energy-efficient, consuming significantly less energy than PoW
- Faster block processing times, resulting in lower transaction fees
- Reduced risk of 51% attacks, as a malicious entity would need to acquire a majority of the cryptocurrency’s supply
Disadvantages:
- Potential for centralization, as validators with larger stakes have higher influence
- Can be vulnerable to “nothing-at-stake” attacks, where validators have no incentive to act honestly
- May not be suitable for cryptocurrencies with high transaction volume
Evolution of Consensus Mechanisms in the Blockchain Landscape
As blockchain technology continues to mature and evolve, both PoW and PoS mechanisms are undergoing significant advancements and refinements. Developers are exploring hybrid approaches, such as Proof of Work with Proof of Stake (PoW/PoS), to leverage the strengths of both mechanisms while mitigating their weaknesses.
PoW/PoS Hybrid Model:
- Combines the security of PoW with the efficiency of PoS
- Reduces energy consumption while maintaining high levels of network security
- Provides a flexible framework for adaptation to changing requirements
Future Implications and Potential Applications
In the lead-up to 2025, the competition between PoW and PoS is expected to intensify as developers and crypto enthusiasts debate the most effective consensus mechanism for different blockchain applications. The choice between the two will depend on factors such as security requirements, energy consumption, transaction volume, and decentralization preferences.
Innovative New Applications and Opportunities:
The evolution of consensus mechanisms is not limited to cryptocurrencies. Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries, and the choice of consensus mechanism will play a critical role in shaping these applications. For instance:
- Supply Chain Management: PoS-based blockchains can provide efficient and tamper-proof tracking of goods, ensuring transparency and trust among stakeholders.
- Healthcare: Hybrid PoW/PoS systems can secure patient data, streamline medical records management, and facilitate secure health data sharing.
- Digital Identity: PoS-based blockchains can empower individuals with control over their digital identities, reducing fraud and protecting privacy.
Strategies for Businesses and Developers
Tips and Tricks for Enterprises:
- Carefully evaluate the specific requirements of your blockchain application before selecting a consensus mechanism.
- Consider hybrid models to optimize security, efficiency, and scalability.
- Stay informed about the latest advancements in consensus mechanisms to adapt to evolving best practices.
- Partner with experienced blockchain developers to ensure a secure and reliable implementation.
Comparison of Proof of Work and Proof of Stake
Table 1: Energy Consumption
| Consensus Mechanism | Energy Consumption |
|---|---|
| Proof of Work | High |
| Proof of Stake | Low |
Table 2: Block Processing Time
| Consensus Mechanism | Block Processing Time |
|---|---|
| Proof of Work | Slow |
| Proof of Stake | Fast |
Table 3: Vulnerability to 51% Attacks
| Consensus Mechanism | Vulnerability to 51% Attacks |
|---|---|
| Proof of Work | High |
| Proof of Stake | Low |
Table 4: Decentralization
| Consensus Mechanism | Decentralization |
|---|---|
| Proof of Work | High |
| Proof of Stake | Potentially Lower |
Pros and Cons of Proof of Work and Proof of Stake
Proof of Work
Pros:
- High security
- Decentralized
- Proven track record
Cons:
- High energy consumption
- Slow block processing times
- Vulnerable to 51% attacks
Proof of Stake
Pros:
- Energy-efficient
- Faster block processing times
- Reduced risk of 51% attacks
Cons:
- Potential for centralization
- Can be vulnerable to “nothing-at-stake” attacks
- May not be suitable for cryptocurrencies with high transaction volume
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Which consensus mechanism is better?
– The choice between PoW and PoS depends on the specific application requirements. PoW provides higher security but consumes more energy, while PoS is more efficient but may have lower levels of decentralization. -
What is the future of consensus mechanisms?
– Hybrid models and advancements in PoS are expected to shape the future of consensus mechanisms, balancing security, efficiency, and scalability. -
Can new consensus mechanisms emerge?
– Yes, researchers are continuously exploring innovative consensus mechanisms to enhance blockchain technology’s capabilities and address emerging challenges. -
How can businesses leverage consensus mechanisms?
– Businesses can leverage consensus mechanisms to build secure and reliable blockchain applications, improving efficiency, transparency, and trust in various industries. -
What are the key differences between PoW and PoS?
– PoW relies on computational power to validate transactions, while PoS uses the concept of staking. PoW is energy-intensive, while PoS is more efficient. PoW has a higher level of security, while PoS is less vulnerable to 51% attacks. -
What are the advantages of PoW over PoS?
– PoW provides higher security due to its computational complexity and decentralization. It has a proven track record with established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. -
What are the disadvantages of PoW compared to PoS?
– PoW consumes high amounts of energy, contributing to environmental concerns. It also has slow block processing times, leading to higher transaction fees. -
What are the advantages of PoS over PoW?
– PoS is energy-efficient and consumes significantly less energy than PoW. It has faster block processing times, resulting in lower transaction fees. PoS reduces the risk of 51% attacks. -
What are the disadvantages of PoS compared to PoW?
– PoS has the potential for centralization, as validators with larger stakes have higher influence. It can be vulnerable to “nothing-at-stake” attacks.