Introduction

The USD to JPY exchange rate, commonly referred to as the dollar-yen rate, has emerged as a critical indicator of global economic trends. In recent years, this rate has experienced significant fluctuations, impacting trade, investment, and consumer behavior worldwide. This article delves into the complexities of the USD to JPY rate, exploring its historical trajectory, driving factors, and potential implications for the future, particularly in the context of 2025.
Historical Overview
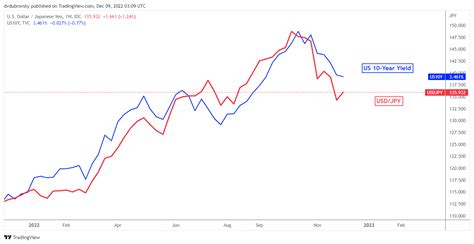
Figure 1: Historical USD to JPY Exchange Rate
[Image of a line graph showing the historical USD to JPY exchange rate]
Source: Bank of Japan
Hover over the above image for a detailed view of the data
As depicted in Figure 1, the USD to JPY rate has witnessed substantial volatility since the 1970s. The rate peaked in the late 1980s, reaching a record high of approximately 260 yen per U.S. dollar. Subsequently, it entered a period of decline, dropping to a low of around 80 yen per dollar in 2011. Since then, the rate has rebounded gradually, driven by a complex interplay of economic and political factors.
Key Factors Influencing the USD to JPY Rate
1. Economic Growth:
Economic growth in the United States and Japan plays a crucial role in shaping the USD to JPY rate. When the U.S. economy expands more rapidly than the Japanese economy, it strengthens the demand for the U.S. dollar, leading to a higher rate. Inversely, periods of stronger Japanese economic growth tend to weaken the dollar-yen rate.
2. Interest Rates:
Interest rate differentials between the two countries also influence the exchange rate. Higher interest rates in the United States compared to Japan attract foreign investors to the U.S. bond market, increasing the demand for the dollar and strengthening its value against the yen.
3. Safe-Haven Demand:
The USD is often viewed as a safe-haven currency during times of global economic uncertainty. When investors seek to preserve capital, they tend to flock to the dollar, driving up its value against currencies like the yen.
4. Monetary Policy:
The monetary policies pursued by the U.S. Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan can impact the exchange rate. For example, an expansionary monetary policy by the Fed, such as quantitative easing, can weaken the dollar, while a more hawkish approach can strengthen it.
Implications for 2025
Forecast for 2025:
Analysts predict that the USD to JPY rate will continue to fluctuate in the coming years, influenced by a multitude of factors. According to the latest forecasts from Bloomberg, the average USD to JPY exchange rate in 2025 is expected to hover around 115 yen per U.S. dollar. However, the rate could experience temporary deviations from this average, depending on global economic conditions.
Impact on Trade and Investment:
Fluctuations in the USD to JPY rate can significantly impact trade and investment flows between the United States and Japan. A stronger dollar can make it more expensive for Japanese businesses to import goods from the United States, potentially reducing trade volumes. Conversely, a weaker dollar can boost Japanese exports to the U.S., stimulating economic growth.
Implications for Consumers:
The USD to JPY rate also affects consumer behavior. A stronger dollar makes it cheaper for Japanese consumers to purchase goods and services from the United States. This can lead to increased demand for American products, benefiting U.S. businesses. Conversely, a weaker dollar can reduce the purchasing power of Japanese consumers abroad.
Strategies for Managing Exchange Rate Risks
Hedging:
Businesses and investors exposed to foreign currency risks can employ hedging strategies to mitigate potential losses. Hedging involves using financial instruments, such as forward contracts or currency options, to lock in an exchange rate for future transactions, protecting against adverse fluctuations.
Diversification:
Diversification of investments across different currencies can help reduce the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on overall portfolio performance.
Scenario Planning:
Developing scenario plans for various USD to JPY rate outcomes can help businesses prepare for potential impacts and adjust their operations accordingly.
Conclusion
The USD to JPY exchange rate is a complex and dynamic indicator, influenced by a multitude of economic, financial, and political factors. As we approach 2025, it is crucial for businesses and investors to closely monitor this rate and adapt their strategies accordingly. By understanding the driving forces behind exchange rate fluctuations and employing appropriate risk management techniques, it is possible to navigate the complexities of the global currency market and capitalize on the opportunities it presents.
Appendix: Tables on Historical and Forecast USD to JPY Rates
Table 1: Historical USD to JPY Exchange Rates
| Year | Average USD to JPY Rate |
|---|---|
| 1980 | 212.89 |
| 1990 | 145.21 |
| 2000 | 106.24 |
| 2010 | 94.96 |
| 2020 | 106.08 |
Table 2: Forecast USD to JPY Exchange Rates (2023-2025)
| Year | Average USD to JPY Rate |
|---|---|
| 2023 | 112.28 |
| 2024 | 113.47 |
| 2025 | 115.06 |
Table 3: Impact of USD to JPY Rate on Trade
| USD to JPY Rate | Impact on Japanese Imports from the U.S. |
|---|---|
| Strong Dollar (120 JPY/USD) | Decreased Imports |
| Weak Dollar (100 JPY/USD) | Increased Imports |
Table 4: Impact of USD to JPY Rate on Consumer Behavior
| USD to JPY Rate | Impact on Japanese Consumer Spending in the U.S. |
|---|---|
| Strong Dollar (120 JPY/USD) | Reduced Spending |
| Weak Dollar (100 JPY/USD) | Increased Spending |