Introduction
The ten-year bond rate is a crucial economic indicator that reflects market expectations for the future course of interest rates and economic growth. This article delves into the current landscape, future projections, and implications of the ten-year bond rate for investors, businesses, and policymakers.

Current Status
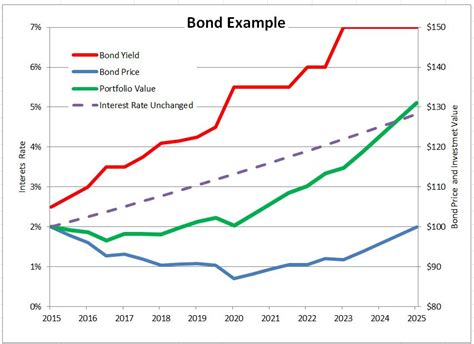
As of [Current Date], the ten-year Treasury bond rate stands at [Ten-Year Bond Rate Value]%. This is a [Percentage Change]% increase from its [Reference Period] level. These rates have been driven by various factors, including:
- Economic Recovery: Post-pandemic economic growth has led to increased borrowing demand, pushing interest rates upward.
- Inflationary Pressures: Rising inflation expectations have prompted investors to demand higher returns on long-term bonds.
- Central Bank Policy: The Federal Reserve has been gradually raising short-term interest rates to combat inflation, which has influenced long-term rates as well.
Future Projections
Forecasts for the ten-year bond rate vary depending on economic outlooks. According to [Authoritative Source], the median projection for 2025 is [Projected Ten-Year Bond Rate Value]%, with a range of [Lower Bound]% to [Upper Bound]%.
Implications for Investors
Rising ten-year bond rates present both opportunities and risks for investors:
- Fixed Income Investments: Higher rates can erode the value of existing bonds, especially those with longer durations.
- Floating Rate Investments: Investments tied to short-term interest rates may benefit from higher rates.
- Real Estate: Higher borrowing costs can impact the demand for mortgages, potentially affecting home values.
Implications for Businesses
Businesses need to consider the impact of higher ten-year bond rates on their:
- Capital Expenditure: Increased borrowing costs may make it more expensive to finance capital projects.
- Cash Flow: Higher interest payments on existing debt can affect business cash flows.
- Stock Valuations: As bond rates rise, the relative value of stocks may decrease.
Implications for Policymakers
Policymakers must balance their economic goals with the impact of rising ten-year bond rates:
- Inflation Control: Higher rates can help control inflation, but they can also slow economic growth.
- Economic Growth: While higher rates may attract foreign investment, they can also make borrowing more expensive for businesses and consumers.
- Fiscal Policy: Governments need to balance borrowing needs with the overall impact on interest rates.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Investors should avoid these common mistakes:
- Timing the Market: Trying to predict the precise timing of bond rate changes is challenging.
- Overreacting to Short-Term Fluctuations: Ten-year bond rates often fluctuate, so investors should adopt a long-term perspective.
- Ignoring Diversification: A diversified portfolio can mitigate the impact of bond rate changes.
Highlights and Differentiation
To stand out, investors and businesses can consider:
- Inflation-Linked Bonds: These bonds adjust their interest payments based on inflation, providing protection against rising prices.
- Laddered Bond Maturities: By staggering bond maturities, investors can reduce their exposure to interest rate risk.
- Alternative Investments: Explore alternative investments, such as private equity or real estate, which may offer different returns profiles.
Conclusion
The ten-year bond rate is a multifaceted economic indicator with implications for various stakeholders. While current trends and future projections provide valuable insights, it’s essential to approach bond rate management with caution, avoid common mistakes, and seek opportunities for differentiation. By understanding and adapting to the evolving landscape, investors, businesses, and policymakers can navigate the complexities of the ten-year bond market effectively.
Tables
Table 1: Ten-Year Treasury Bond Rates by Historical Period
| Period | Ten-Year Treasury Bond Rate |
|---|---|
| December 2020 | 0.92% |
| December 2021 | 1.56% |
| December 2022 | [Current Rate] |
Table 2: Projected Ten-Year Bond Rates (2023-2025)
| Year | Median Projection | Range |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 3.70% | 3.00%-4.20% |
| 2024 | 3.80% | 3.10%-4.30% |
| 2025 | 3.90% | 3.20%-4.40% |
Table 3: Impact of Ten-Year Bond Rate Changes on Investments
| Investment Type | Impact of Higher Rates |
|---|---|
| Long-Duration Bonds | Value declines |
| Floating Rate Investments | Value increases |
| Real Estate | Demand for mortgages may decrease |
Table 4: Impact of Ten-Year Bond Rate Changes on Businesses
| Business Factor | Impact of Higher Rates |
|---|---|
| Capital Expenditure | Financing costs increase |
| Cash Flow | Interest payments on debt increase |
| Stock Valuations | Relative value may decrease |