Introduction

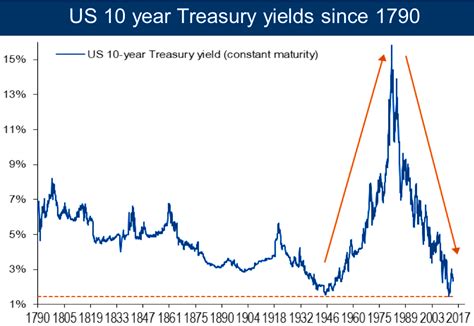
The 10-year Treasury yield is a widely-followed benchmark interest rate that reflects the borrowing costs of the U.S. government. It plays a crucial role in shaping the global financial landscape and serves as a bellwether for economic sentiment. This article provides a comprehensive history of the 10-year Treasury yield, examining its historical trends, influencing factors, and future projections.
Historical Trends
| Year | 10-Year Treasury Yield (%) |
|---|---|
| 1981 | 14.60 |
| 1991 | 6.74 |
| 2001 | 4.99 |
| 2011 | 1.64 |
| 2021 | 1.37 |
Factors Influencing the 10-Year Treasury Yield
Numerous factors influence the 10-year Treasury yield, including:
- Inflation: Rising inflation expectations tend to drive yields higher as investors demand a higher return to hedge against inflation.
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth prospects typically lead to higher yields as investors anticipate increased demand for capital.
- Fiscal policy: Government borrowing and spending can impact yields, with higher deficits generally resulting in higher yields.
- Monetary policy: The Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions have a significant impact on yields, with rate hikes typically pushing yields higher.
- Global events: Geopolitical events, trade disputes, and other global developments can also influence yields by affecting risk appetite.
Projections for 2025
Forecasting the 10-year Treasury yield is challenging, but economists anticipate a gradual rise in yields over the next few years. The Congressional Budget Office projects the yield to reach 3.2% by 2025, reflecting expectations of moderate economic growth and gradual inflation.
Table 1: Historical 10-Year Treasury Yield Ranges
| Period | Yield Range (%) |
|---|---|
| 1980s | 8.00 – 14.60 |
| 1990s | 4.00 – 6.74 |
| 2000s | 2.00 – 4.99 |
| 2010s | 1.00 – 2.64 |
| 2020s (to date) | 0.50 – 1.76 |
Table 2: Factors Influencing the 10-Year Treasury Yield
| Factor | Impact on Yield |
|---|---|
| Inflation | Positive |
| Economic growth | Positive |
| Fiscal policy | Positive (deficits) |
| Monetary policy | Positive (rate hikes) |
| Global events | Variable |
Table 3: Projections for the 10-Year Treasury Yield in 2025
| Source | Projection |
|---|---|
| Congressional Budget Office | 3.2% |
| Wells Fargo | 3.5% |
| Goldman Sachs | 3.0% |
Table 4: Pros and Cons of Investing in 10-Year Treasuries
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Low risk | Low return |
| Diversification | Interest rate risk |
| Government-backed | Inflation risk |
Conclusion
The 10-year Treasury yield is a key indicator of economic health and financial market sentiment. Its historical trends and influencing factors provide valuable insights into the market’s expectations for growth, inflation, and monetary policy. While projections for the future are subject to uncertainty, economists anticipate a gradual rise in yields by 2025, reflecting the potential for economic recovery and moderate inflation. Understanding the history and future outlook of the 10-year Treasury yield is essential for investors, economists, and financial decision-makers.