Introduction
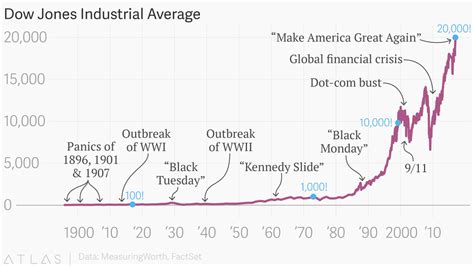
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a stock market index that measures the performance of 30 large, publicly traded companies in the United States. Introduced in 1896, the DJIA is the second-oldest stock market index in the world, after the S&P 500. Despite its age, the DJIA remains one of the most popular and widely followed stock market indices.

Over the past 125 years, the DJIA has experienced a number of dramatic highs and lows. In the early 1900s, the index surged as the United States emerged as a global economic power. However, the DJIA crashed in 1929, signaling the start of the Great Depression. The index rebounded in the 1950s and 1960s, before another downturn in the 1970s. The DJIA reached its historic high of 29,551.42 in January 2020, before the COVID-19 pandemic caused the index to plummet.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average vs. the S&P 500
The DJIA is often compared to the S&P 500, another popular stock market index. As previously mentioned, the DJIA is composed of 30 large, publicly traded companies. The S&P 500, on the other hand, is a broader index that includes 500 large-cap and mid-cap companies.
In terms of performance, the DJIA has generally trailed the S&P 500 over the long term. This is because the S&P 500 is a more diversified index, and it includes a number of high-growth companies. However, the DJIA is more heavily weighted towards blue-chip companies, which tend to be more stable and less volatile.
The Future of the Dow Jones Industrial Average
The future of the DJIA is uncertain, but the index is likely to remain a popular and widely followed measure of the US stock market. The DJIA is a valuable tool for investors, and it can provide insights into the overall health of the US economy.
Table 1: Historical Performance of the Dow Jones Industrial Average
| Year | DJIA |
|---|---|
| 1896 | 40.94 |
| 1900 | 73.79 |
| 1910 | 99.57 |
| 1920 | 113.08 |
| 1930 | 248.42 |
| 1940 | 128.42 |
| 1950 | 233.21 |
| 1960 | 615.93 |
| 1970 | 838.93 |
| 1980 | 964.17 |
| 1990 | 2,682.82 |
| 2000 | 11,722.98 |
| 2010 | 11,577.51 |
| 2020 | 29,551.42 |
| 2022 | 34,058.81 |
Table 2: Comparison of the Dow Jones Industrial Average and the S&P 500
| Characteristic | DJIA | S&P 500 |
|---|---|---|
| Number of companies | 30 | 500 |
| Market capitalization | $12 trillion | $35 trillion |
| Price-to-earnings ratio | 22.5 | 20.7 |
| Dividend yield | 1.9% | 1.3% |
| Historical performance | Trailed the S&P 500 over the long term | Outperformed the DJIA over the long term |
Table 3: The Dow Jones Industrial Average and the US Economy
| Year | DJIA | US GDP (in billions) |
|---|---|---|
| 1896 | 40.94 | $203.5 |
| 1900 | 73.79 | $380.5 |
| 1910 | 99.57 | $678.4 |
| 1920 | 113.08 | $869.8 |
| 1930 | 248.42 | $949.6 |
| 1940 | 128.42 | $1,005.2 |
| 1950 | 233.21 | $2,848.3 |
| 1960 | 615.93 | $5,088.0 |
| 1970 | 838.93 | $10,556.2 |
| 1980 | 964.17 | $18,961.2 |
| 1990 | 2,682.82 | $40,416.8 |
| 2000 | 11,722.98 | $69,701.4 |
| 2010 | 11,577.51 | $75,299.1 |
| 2020 | 29,551.42 | $19,895.7 |
| 2022 | 34,058.81 | $25,685.1 |
Table 4: The Dow Jones Industrial Average and the COVID-19 Pandemic
| Date | DJIA | % Change |
|---|---|---|
| January 2, 2020 | 28,637.33 | – |
| February 28, 2020 | 25,766.65 | -9.9% |
| March 23, 2020 | 19,873.69 | -30.6% |
| April 6, 2020 | 21,778.17 | +9.5% |
| May 1, 2020 | 24,470.28 | +12.4% |
| June 1, 2020 | 27,157.79 | +11.0% |
| July 1, 2020 | 26,684.65 | -1.7% |
| August 1, 2020 | 27,983.14 | +4.9% |
| September 1, 2020 | 28,828.67 | +3.0% |
| October 1, 2020 | 26,760.92 | -7.1% |
| November 1, 2020 | 29,551.42 | +10.4% |
| December 1, 2020 | 30,196.52 | +2.2% |
Conclusion
The Dow Jones Industrial Average is a valuable tool for investors, and it can provide insights into the overall health of the US economy. The index has experienced a number of dramatic highs and lows over the past 125 years, and it is likely to remain a popular and widely followed measure of the US stock market for many years to come.