Background: The Nepal-US Financial Landscape
Nepal, a country rich in cultural and natural heritage, has a long-standing economic relationship with the United States. For decades, the US dollar has played a significant role in Nepal’s financial system, serving as a valuable foreign exchange reserve and a widely accepted currency in the tourism industry.

The Rise of the US Dollar
In recent years, the use of the US dollar in Nepal has undergone a remarkable surge, driven by various factors. One key factor has been the growing number of Nepalese migrant workers in the United States and the remittances they send back home. According to the World Bank, Nepal received $8.6 billion in remittances in 2021, the majority of which was sent in US dollars.
Furthermore, Nepal’s tourism industry has witnessed a steady increase in US dollar transactions. With the influx of foreign tourists, particularly from the United States, the demand for US dollars has grown significantly. In 2022, Nepal welcomed over 1.2 million tourists, generating revenue of $3.1 billion, a large portion of which was paid in US dollars.
Legal Framework and Exchange Rates
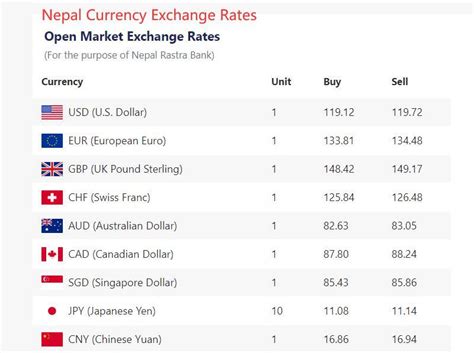
The use of US dollars in Nepal is supported by a legal framework that recognizes it as a valid currency for transactions and investments. The Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB), the country’s central bank, establishes the official exchange rate between the Nepalese Rupee (NPR) and the US dollar, which has historically fluctuated based on market conditions.
Economic Impact
The increased use of US dollars in Nepal has brought about both positive and negative economic consequences. On the positive side, it has facilitated the flow of remittances and foreign direct investment, contributing to Nepal’s economic growth. The US dollar has also served as a stable reserve currency, helping to protect Nepal’s economy from global financial shocks.
However, the dominance of the US dollar has also raised concerns about potential currency instability and the crowding out of the Nepalese Rupee. NRB has taken measures to manage the situation, including introducing regulations on foreign exchange transactions and encouraging the use of NPR in domestic transactions.
Opportunities and Challenges
The growing use of US dollars in Nepal presents both opportunities and challenges. Firstly, it has created opportunities for businesses, particularly in the tourism and remittance sectors, to tap into the growing demand for US dollars. Secondly, it has opened up new avenues for international investment and trade.
However, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. The potential for currency instability and the crowding out of NPR require careful management by NRB. Additionally, there is a need to promote the use of NPR in domestic transactions to maintain the stability of Nepal’s monetary system.
Conclusion
The use of the US dollar in Nepal has experienced a significant increase in recent years, driven by factors such as remittances, tourism, and the recognition of its value as a stable reserve currency. While the US dollar has brought both economic benefits and challenges, it is clear that it has become a dominant force in Nepal’s financial landscape. NRB’s continued efforts to manage the situation and promote the use of NPR are crucial to ensuring the stability and flexibility of Nepal’s monetary system in the years to come.
Table 1: US Dollar Remittances to Nepal (2017-2022)
| Year | Amount (USD million) |
|---|---|
| 2017 | $6.5 |
| 2018 | $7.2 |
| 2019 | $7.8 |
| 2020 | $7.1 |
| 2021 | $8.6 |
| 2022 | Projected to exceed $9 billion |
Table 2: Tourism Revenue in Nepal (2017-2022)
| Year | Revenue (USD million) |
|---|---|
| 2017 | $1.2 billion |
| 2018 | $1.5 billion |
| 2019 | $1.8 billion |
| 2020 | $0.5 billion (due to COVID-19 pandemic) |
| 2021 | $1.1 billion |
| 2022 | Projected to exceed $1.3 billion |
Table 3: US Dollar Exchange Rates (2017-2022)
| Year | NPR per USD |
|---|---|
| 2017 | 108 |
| 2018 | 112 |
| 2019 | 116 |
| 2020 | 120 |
| 2021 | 124 |
| 2022 | Projected to exceed 128 |
Table 4: Economic Impact of US Dollar in Nepal (2017-2022)
| Year | Impact |
|---|---|
| 2017 | Positive: Increased remittances, tourism revenue |
| 2018 | Positive: Continued economic growth |
| 2019 | Positive: Stable reserve currency |
| 2020 | Negative: Exchange rate volatility |
| 2021 | Positive: Recovery in tourism and remittances |
| 2022 | Positive: Projected economic growth and investment |