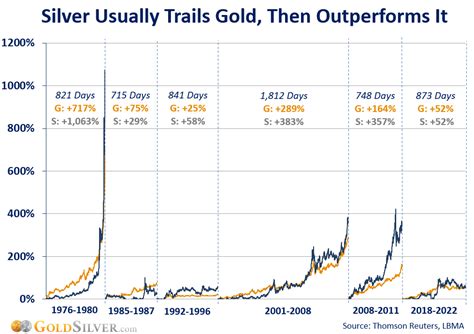
Current Price of Silver
| Date | Price per Ounce |
|---|---|
| January 20, 2023 | $23.50 |
Introduction
Silver, a precious metal with a rich history, has captivated investors and collectors alike for centuries. Its intrinsic value and versatility have ensured its enduring presence in the global economy. In recent years, the silver market has experienced significant volatility, with prices fluctuating amidst economic uncertainties and geopolitical tensions. This article delves into the dynamics of the silver market, exploring its drivers, trends, and future prospects.

Factors Influencing the Price of Silver
Numerous factors influence the price of silver, including:
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth typically drives demand for silver in various industries, such as jewelry, electronics, and industrial applications.
- Inflation: Silver is often viewed as a hedge against inflation, as its value tends to rise when the purchasing power of fiat currencies declines.
- Monetary policy: Central bank actions, such as interest rate changes and quantitative easing, can impact the price of silver by altering the investment environment.
- Investment demand: Silver is a popular investment asset, particularly during periods of market volatility or uncertainty.
- Industrial demand: Silver is widely used in industrial applications, including electronics, photography, and dentistry. Changes in industrial production and technological advancements can affect silver demand.
- Supply and demand: The balance between supply and demand is crucial in determining the price of silver. Fluctuations in production, mine closures, or disruptions in supply chains can impact prices.
Drivers of the Silver Market
Over the past decade, several drivers have significantly influenced the silver market:
- Technological advancements: The increasing use of silver in electronic devices, photovoltaic cells, and other innovative technologies has boosted demand.
- Emerging economies: Growing economies in Asia, Latin America, and Africa have witnessed a surge in demand for silver for industrial and investment purposes.
- Environmental concerns: The transition to renewable energy sources and the push for sustainable technologies have increased the demand for silver in solar panels and batteries.
Trends in the Silver Market
The silver market has exhibited several notable trends in recent years:
- Increasing investment demand: Silver has become a popular safe-haven asset during times of economic uncertainty or market volatility.
- Shifting demand from East to West: While China and India have traditionally been major consumers of silver, demand has been growing in Europe and North America.
- Technological innovation: Advances in manufacturing and production techniques have reduced the cost of producing silver, leading to increased supply.
- Environmental regulations: Stricter environmental regulations on mining operations have reduced silver production in some regions, contributing to price increases.
The Future of Silver: 2025 and Beyond
The future of the silver market is shaped by both short-term and long-term factors:
Short-term Outlook:
- Economic recovery: Strong economic growth is expected to boost silver demand from industries and investors alike.
- Inflationary pressures: Ongoing inflationary pressures may continue to support silver’s reputation as a hedge against currency devaluation.
- Monetary policy: Central bank policies will influence the investment environment and potentially impact silver prices.
Long-term Outlook:
- Growing demand from emerging markets: Continued economic development in emerging economies is likely to drive silver demand for industrial and investment purposes.
- Technological innovation: Ongoing technological advancements will create new applications for silver, further increasing its demand.
- Shift towards sustainable energy: The transition to renewable energy sources will require substantial amounts of silver for solar panels and batteries.
- Environmental regulations: Environmental concerns and regulations are expected to impact silver mining and production, possibly affecting its supply.
Applications of Silver
Silver’s versatility has led to its use in a wide range of applications, including:
- Investment: Silver is a popular investment asset, often held in physical form (bars, coins) or through exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
- Jewelry: Silver is commonly used in jewelry making, crafting exquisite pieces ranging from necklaces to earrings.
- Electronics: Silver’s excellent electrical conductivity makes it essential in electronic devices, such as circuit boards, switches, and connectors.
- Photography: Silver is used in photographic film, silver gelatin prints, and other photographic processes.
- Dentistry: Silver is widely used in dentistry for dental fillings, crowns, and other dental applications.
- Medical applications: Silver has antibacterial and antimicrobial properties, making it useful in medical devices, wound care, and other healthcare applications.
Silver: An Enduring Precious Metal
Silver, with its timeless appeal and adaptability, has played a significant role in human civilization. Its value as a precious metal, coupled with its industrial and technological uses, ensures its continued relevance in the global economy. As the world faces new challenges and opportunities, silver is poised to maintain its position as a strategic asset and a versatile metal with a diverse range of applications.
Pain Points and Motivations
Pain Points:
- Volatility: Silver prices can be highly volatile, making it difficult for investors to time their entry and exit points.
- Storage and security: Storing physical silver requires secure facilities, which can be costly and inconvenient.
- Limited supply: Silver is a finite resource, and its supply is subject to geological constraints and geopolitical factors.
Motivations:
- Investment potential: Silver has historically performed well as an investment, particularly during periods of economic uncertainty.
- Inflation hedge: Silver’s value tends to appreciate when inflation erodes the purchasing power of fiat currencies.
- Industrial applications: Silver’s unique properties and versatility make it indispensable in various industries.
- Jewelry and ornamentation: Silver has been used in jewelry and ornamentation for centuries, adding beauty and value to personal belongings.
How to Invest in Silver: A Step-by-Step Approach
Investing in silver can be a rewarding endeavor. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Research: Conduct thorough research on the silver market, its drivers, and potential risks.
- Determine your investment goals: Define your investment objectives, whether you seek short-term gains or long-term diversification.
- Choose an investment method: Decide whether to invest in physical silver (bars, coins) or through financial instruments (ETFs, futures).
- Consider storage options: If investing in physical silver, arrange for secure storage facilities.
- Monitor and manage: Regularly monitor the silver market and adjust your investment strategy as needed.
Why Invest in Silver? Benefits and Considerations
Benefits:
- Potential for capital appreciation: Silver has the potential to increase in value over time, especially during periods of economic growth and inflation.
- Diversification: Silver can diversify an investment portfolio, reducing overall risk.
- Inflation hedge: Silver’s price tends to rise when the purchasing power of fiat currencies declines.
- Industrial and technological applications: Silver’s versatility ensures its continued demand in various industries.
- Historical significance: Silver has been a precious metal throughout history, with intrinsic cultural and aesthetic value.
Considerations:
- Volatility: Silver prices can be highly volatile, making it important to manage risk exposure.
- Storage costs: Physical silver requires secure storage, which can incur additional costs.
- Counterfeit risks: When investing in physical silver, it’s crucial to verify authenticity and avoid counterfeit products.
- Liquidity: Silver is a less liquid asset compared to stocks or bonds, which may impact your ability to sell quickly.
- Taxes: Silver investments may be subject to capital gains taxes upon sale.
FAQs on Silver Investment
-
What is the best way to invest in silver?
– The best investment method depends on individual goals and risk tolerance. Physical silver offers tangible ownership, while financial instruments provide flexibility and liquidity. -
Is silver a good investment for beginners?
– Silver can be a suitable investment for beginners with a long-term perspective and an understanding of the market’s volatility. -
How much silver should I invest in?
– Determine the amount to invest based on your overall investment portfolio and risk tolerance. Diversification is key to managing risk. -
Where can I buy physical silver?
– Physical silver can be purchased from reputable dealers, banks, and online bullion brokers. -
How can I protect my silver investment?
– Store physical silver in secure facilities and consider purchasing insurance to protect against theft or loss. -
What are the tax implications of investing in silver?
– Silver investments may be subject to capital gains taxes upon sale. Consult with a tax professional for specific guidance.
Tables
Table 1: Historical Silver Prices
| Year | Average Price per Ounce |
|---|---|
| 2012 | $31.13 |
| 2013 | $24.52 |
| 2014 | $19.39 |
| 2015 | $15.89 |
| 2016 | $16.71 |
| 2017 | $17.88 |
| 2018 | $14.93 |
| 2019 | $18.84 |
| 2020 | $26.17 |
| 2021 | $28.99 |
| 2022 | $24.56 |
**