Introduction
Long-term capital gains tax (LTCG) plays a crucial role in shaping investment decisions and optimizing financial outcomes. As we approach 2024, understanding the intricate details of LTCG is paramount to maximizing returns and minimizing tax liabilities. This comprehensive guide will delve into the complexities of LTCG, providing a roadmap for investors to navigate the tax landscape and reap significant financial benefits.

What is Long-Term Capital Gains Tax?
LTCG refers to the tax imposed on profits from the sale of capital assets, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, held for more than a year. The tax rate for LTCG is typically lower than the ordinary income tax rate. However, the rate depends on an individual’s taxable income bracket and the type of asset sold.
Key Changes in LTCG Tax for 2024
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017 brought about significant changes to LTCG tax rates. However, the TCJA is set to expire in 2025. If Congress does not extend or amend the TCJA, LTCG tax rates will revert to their pre-TCJA levels in 2026.
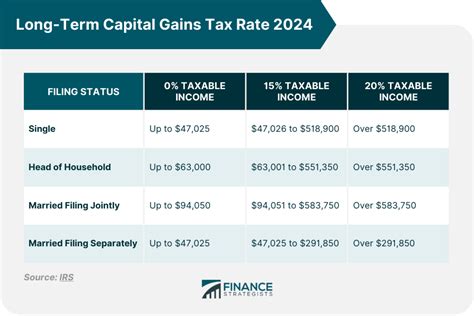
For tax years 2023 and 2024, the LTCG tax rates are as follows:
| Filing Status | LTCG Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Single | 0%, 15%, or 20% |
| Married Filing Jointly | 0%, 15%, or 20% |
| Married Filing Separately | 0%, 15%, or 20% |
| Head of Household | 0%, 15%, or 20% |
Implications for Investors
The current LTCG tax rates offer investors significant advantages compared to the pre-TCJA rates. The lower tax rates provide an incentive for long-term investment and capital accumulation. Investors can benefit from these lower rates by:
- Holding on to investments for longer periods
- Realizing capital gains in lower tax brackets
- Utilizing tax-advantaged investment accounts
Maximizing LTCG Returns
To maximize LTCG returns, investors should adopt a strategic approach that includes:
- Long-Term Investment Horizon: Holding investments for at least a year qualifies for the favorable LTCG tax rates.
- Tax-Loss Harvesting: Selling assets that have incurred a loss to offset capital gains and reduce taxes.
- Charitable Giving: Donating appreciated assets to eligible charities can eliminate capital gains tax.
- IRA and 401(k) Contributions: Investing in tax-advantaged retirement accounts postpones capital gains tax until withdrawals are made.
Comparison of Pre- and Post-TCJA LTCG Tax Rates
The table below compares the LTCG tax rates before and after the TCJA:
| Filing Status | Pre-TCJA LTCG Tax Rate | Post-TCJA LTCG Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Single | 15% or 20% | 0%, 15%, or 20% |
| Married Filing Jointly | 15% or 20% | 0%, 15%, or 20% |
| Married Filing Separately | 15% or 20% | 0%, 15%, or 20% |
| Head of Household | 15% or 20% | 0%, 15%, or 20% |
Future Trends and Outlook
The future of LTCG tax is uncertain. If Congress does not extend or amend the TCJA, LTCG tax rates will revert to their pre-TCJA levels in 2026. However, several factors could influence future LTCG tax policies, including:
- Federal budget deficits
- Economic growth and revenue projections
- Political and ideological preferences
Recommendations for Investors
In light of the potential changes to LTCG tax rates in 2026, investors should consider the following recommendations:
- Review Investment Portfolio: Assess the current portfolio and identify assets that may trigger LTCG in the future.
- Plan for Tax Liability: Estimate potential LTCG tax liability and explore strategies to minimize taxes.
- Consider Tax-Advantaged Investments: Utilize tax-advantaged investment accounts to defer or eliminate LTCG tax.
- Consult with a Tax Professional: Seek advice from a qualified tax professional to navigate the complexities of LTCG regulations.
Conclusion
Long-term capital gains tax is a critical consideration for investors seeking to maximize returns and minimize tax liabilities. Understanding the current LTCG tax rates and potential future changes empowers investors to make informed decisions and optimize their financial outcomes. By adopting a strategic approach and leveraging tax-advantaged strategies, investors can reap the benefits of LTCG and achieve long-term financial success.
FAQs
-
What is the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains?
* Short-term capital gains are taxed at ordinary income tax rates, while long-term capital gains are taxed at lower rates. -
How do I calculate my LTCG tax liability?
* The LTCG tax liability is calculated by multiplying the capital gain by the applicable LTCG tax rate. -
Can I avoid LTCG tax?
* Yes, contributing to tax-advantaged retirement accounts, such as IRAs and 401(k)s, can postpone or eliminate LTCG tax. -
What happens if the TCJA is not extended?
* If the TCJA is not extended, LTCG tax rates will revert to their pre-TCJA levels in 2026.