USD-INR: Tracking the Fluctuating Exchange Rate

The USD-INR exchange rate is the value of the Indian Rupee (INR) in terms of the United States Dollar (USD). It indicates how many rupees are needed to purchase one US dollar. This exchange rate plays a crucial role in international trade and investment between India and the rest of the world.
The USD-INR exchange rate is influenced by a complex interplay of economic, political, and social factors. These include:
- Inflation: Changes in the inflation rates of India and the US impact the exchange rate. Higher inflation in India relative to the US leads to a weaker rupee.
- Interest Rates: The central banks of India and the US set interest rates, which affect the attractiveness of investing in each country. Higher interest rates in India attract foreign investment, strengthening the rupee.
- Foreign Exchange Reserves: The amount of foreign exchange reserves held by the Reserve Bank of India influences the supply and demand for dollars, thereby affecting the exchange rate.
- Political Stability: Political instability in India or the US can lead investors to sell Indian assets, weakening the rupee.
- Demand for Indian Goods and Services: When the demand for Indian goods and services increases, the rupee tends to appreciate against the dollar.
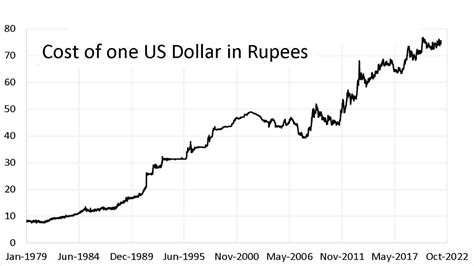
Over the past decade, the USD-INR exchange rate has exhibited significant fluctuations. The rupee strengthened during periods of economic growth and stability in India, such as from 2004 to 2008. However, the rupee weakened during periods of economic uncertainty, such as the global financial crisis of 2008 and the COVID-19 pandemic of 2020.
The USD-INR exchange rate has a significant impact on India’s economy:
- Exports and Imports: A stronger rupee makes Indian exports more expensive, potentially reducing demand. Conversely, a weaker rupee makes imports cheaper, boosting domestic consumption.
- Foreign Direct Investment: A stable exchange rate environment encourages foreign direct investment in India.
- Inflation: Exchange rate fluctuations can affect the prices of imported goods, contributing to inflation or deflation.
- Sovereign Debt: India’s external debt is denominated in dollars. A weaker rupee increases the cost of servicing this debt.
Economists predict that the USD-INR exchange rate will continue to fluctuate in 2025. The following factors will influence these fluctuations:
- India’s Economic Growth: Strong economic growth in India will support the rupee.
- Inflation: The Reserve Bank of India’s efforts to control inflation will indirectly strengthen the rupee.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates in India will make it more attractive for foreign investors to invest in the country, strengthening the rupee.
- Global Economic Conditions: Global economic uncertainty or a recession in the US could weaken the rupee as investors seek safe-haven assets.
Businesses and individuals can adopt strategies to manage currency risk associated with the USD-INR exchange rate:
- Hedging: Use financial instruments such as forward contracts or currency options to lock in an exchange rate for future transactions.
- Diversification: Convert some assets into different currencies to reduce the impact of exchange rate fluctuations.
- Natural Hedging: Engage in international transactions that create natural offsets in foreign currency revenue and expenses.
As of July 2023, the USD-INR exchange rate is approximately 79.50. The Reserve Bank of India is closely monitoring the exchange rate and will intervene if necessary to maintain stability.
To ensure a stable and competitive exchange rate in the long term, the government should focus on the following measures:
- Promote Economic Growth: Sustained economic growth will increase the demand for rupees and strengthen the exchange rate.
- Control Inflation: Maintaining low inflation will reduce the pressure on the rupee to depreciate.
- Attract Foreign Investment: Create a conducive environment for foreign direct investment, which will bring in dollars and strengthen the rupee.
- Manage External Debt: Prudently manage India’s external debt to minimize the impact of currency fluctuations.
The USD-INR exchange rate is a dynamic and complex aspect of the Indian economy. Understanding the factors that influence this exchange rate and adopting appropriate strategies to manage currency risk is crucial for businesses and individuals operating in the international market. By implementing effective policies and fostering economic growth, India can maintain a stable and competitive exchange rate that supports its development aspirations.
- Reserve Bank of India: https://www.rbi.org.in/
- World Bank: https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/india
- International Monetary Fund: https://www.imf.org/en/Countries/IND
Table 1: USD-INR Exchange Rate History
| Year | Exchange Rate |
|---|---|
| 2005 | 44.60 |
| 2010 | 45.30 |
| 2015 | 63.50 |
| 2020 | 74.00 |
| 2023 | 79.50 |
Table 2: Factors Influencing USD-INR Exchange Rate
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Inflation | Changes in the price level |
| Interest Rates | Set by central banks |
| Foreign Exchange Reserves | Amount of foreign currency held by RBI |
| Political Stability | Events affecting investor confidence |
| Demand for Indian Goods and Services | Impact on exports and imports |
Table 3: Impact of USD-INR Exchange Rate on India’s Economy
| Impact | Effect |
|---|---|
| Exports | Affects competitiveness |
| Imports | Affects consumer prices |
| Foreign Direct Investment | Influences investment decisions |
| Inflation | Can contribute to inflation or deflation |
| Sovereign Debt | Impacts servicing costs |
Table 4: Strategies for Managing Currency Risk
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Hedging | Using financial instruments to lock in exchange rate |
| Diversification | Converting assets into different currencies |
| Natural Hedging | Engaging in international transactions with offsets |