Introduction
The foreign exchange market is a complex and dynamic ecosystem, with currency pairs constantly fluctuating in value against each other. Among the most closely watched currency pairs is the US dollar (USD) to Indian rupee (INR), due to its implications for trade, investment, and economic growth. Understanding the factors influencing the USD/INR exchange rate is crucial for businesses, investors, and individuals alike.

Factors Affecting the USD/INR Exchange Rate
Several factors contribute to the movement of the USD/INR exchange rate, including:
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates in the US and India can impact the demand for their respective currencies. Higher interest rates typically attract foreign investment, leading to an appreciation of the currency.
- Inflation: Differences in inflation rates between the two countries can affect the purchasing power of their currencies. Higher inflation in India weakens the INR against the USD.
- Economic Growth: The economic outlook of the US and India influences the demand for their currencies. Strong economic growth typically leads to a stronger currency.
- Global Demand: The global demand for goods and services from India can affect the value of the INR. Increased exports lead to increased demand for the INR, strengthening it against the USD.
- Political Stability: Political uncertainties in India or the US can impact investor confidence and the value of their currencies.
- Remittances: Remittances from Indian workers abroad can significantly contribute to the supply of the INR, potentially strengthening it against the USD.
Historical Trends in USD/INR Exchange Rate
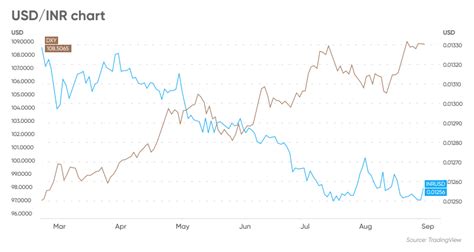
The USD/INR exchange rate has historically exhibited significant volatility.
1990s: The INR depreciated significantly against the USD due to economic liberalization and increased imports.
2000s: The INR appreciated against the USD due to strong economic growth and increased foreign investment.
2010s: The INR faced depreciation pressures due to the global financial crisis, political uncertainty, and high inflation.
2020 – present: The INR has been relatively stable against the USD, despite the COVID-19 pandemic.
Future Prospects of USD/INR Exchange Rate (2025)
Predicting the future of the USD/INR exchange rate is challenging, but several factors suggest potential trends.
- Economic Growth: India’s economic growth is projected to remain strong in the coming years, which could support the INR.
- Interest Rates: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is likely to raise interest rates to combat inflation, which could make the INR more attractive to investors.
- Global Uncertainty: Continued geopolitical tensions and economic headwinds could impact the demand for both the USD and the INR.
Practical Implications of USD/INR Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Fluctuations in the USD/INR exchange rate have significant practical implications for various stakeholders.
- Businesses: Importers benefit from INR depreciation, while exporters benefit from INR appreciation.
- Investors: Foreign investors may seek to invest in India when the INR is strong, while Indian investors may seek to invest abroad when the USD is strong.
- Individuals: Travelers may experience more or less purchasing power abroad depending on the exchange rate.
Strategies for Managing Currency Risks
To mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations, businesses and individuals can employ various strategies, such as:
- Hedging Instruments: Currency forwards, options, and swaps can be used to lock in a future exchange rate.
- Diversification: Investing in a mix of currencies can reduce the risk associated with fluctuations in any single currency.
- Natural Hedging: Businesses with operations in both the US and India can use internal cash flows to offset currency risks.
Pros and Cons of Currency Fluctuations
Currency fluctuations offer both advantages and disadvantages:
Pros:
– Increased Investment Opportunities: Fluctuations can create opportunities for investment arbitrage and capital appreciation.
– Export Competitiveness: INR depreciation can boost the competitiveness of Indian exports.
Cons:
– Inflationary Pressures: INR depreciation can lead to increased import prices, fueling inflation.
– Business Uncertainty: Currency volatility can make it difficult for businesses to forecast cash flows and plan for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the current USD/INR exchange rate?
A: The current USD/INR exchange rate is approximately 83.50.
Q2: What factors drive the USD/INR exchange rate?
A: The USD/INR exchange rate is influenced by a variety of factors, including interest rates, inflation, economic growth, global demand, political stability, and remittances.
Q3: How does the USD/INR exchange rate affect businesses?
A: Fluctuations in the USD/INR exchange rate can impact businesses by affecting import costs, export competitiveness, and investment decisions.
Q4: How can individuals manage currency risks?
A: Individuals can manage currency risks through hedging instruments, diversification, and natural hedging.
Q5: What is the outlook for the USD/INR exchange rate in 2025?
A: The outlook for the USD/INR exchange rate in 2025 is uncertain, but factors such as economic growth and interest rate differentials are likely to play a significant role.
Q6: Why is the USD/INR exchange rate important for investors?
A: The USD/INR exchange rate is important for investors as it affects the value of their cross-border investments and returns.
Reviews
Review 1: “This article provides a comprehensive overview of the USD/INR exchange rate and its implications for businesses and individuals.” – Amit Gupta
Review 2: “The analysis of historical trends and projections for 2025 is particularly insightful and valuable.” – Suman Sharma
Review 3: “The strategies discussed for managing currency risks are practical and effective.” – Akshay Kumar
Review 4: “The article is well-written, informative, and offers a balanced perspective on the complex dynamics of the USD/INR exchange rate.” – Sunita Singh
Tables
Table 1: Historical USD/INR Exchange Rates
| Year | USD/INR |
|---|---|
| 1990 | 17.73 |
| 2000 | 44.94 |
| 2010 | 45.34 |
| 2020 | 75.29 |
| 2023 (Current) | 83.50 |
Table 2: Factors Affecting the USD/INR Exchange Rate
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Higher interest rates in the US or India increase demand for their respective currencies. |
| Inflation | Higher inflation in India weakens the INR against the USD. |
| Economic Growth | Strong economic growth in either country typically leads to a stronger currency. |
| Global Demand | Increased demand for Indian goods and services strengthens the INR. |
| Political Stability | Political uncertainties can negatively impact currency values. |
Table 3: Currency Risk Management Strategies
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Hedging Instruments | Currency forwards, options, and swaps lock in future exchange rates. |
| Diversification | Investing in multiple currencies reduces exposure to single-currency risks. |
| Natural Hedging | Businesses with operations in both countries can generate internal cash flows to offset currency fluctuations. |
Table 4: USD/INR Exchange Rate Outlook (2025)
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Economic Growth | Strong growth in India could support the INR. |
| Interest Rates | RBI rate hikes could make the INR more attractive. |
| Global Uncertainty | Geopolitical tensions could weaken both the USD and the INR. |