Introduction
The United States dollar (USD) and the Indian rupee (INR) are two of the most important currencies in the world. The USD is the world’s reserve currency, while the INR is the seventh most traded currency. The exchange rate between the two currencies has a significant impact on trade and investment, as well as on the lives of individuals and businesses in both countries.

In this article, we will take a comprehensive look at the USD/INR exchange rate, examining its historical trends, current drivers, and future prospects. We will also provide insights into the factors that influence the exchange rate and discuss strategies for managing currency risk.
Historical Trends
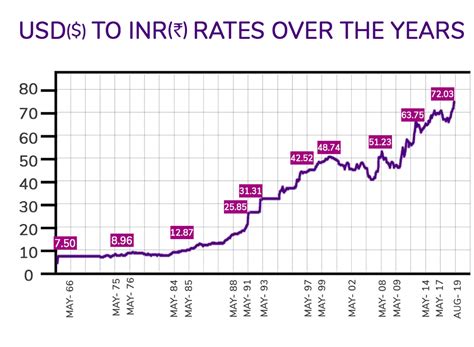
The USD/INR exchange rate has fluctuated significantly over the years. In the early 1990s, one USD was worth around 25 INR. By 2000, the value of the INR had depreciated to around 45 per USD. In the years that followed, the INR continued to depreciate against the USD, reaching a low of around 68 per USD in 2013.
However, in recent years, the INR has appreciated against the USD. In 2022, one USD was worth around 79 INR. This appreciation has been driven by a number of factors, including India’s strong economic growth, rising foreign direct investment, and the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) efforts to stabilize the currency.
Current Drivers
The USD/INR exchange rate is determined by a number of factors, including:
- Economic growth: India’s strong economic growth has led to increased demand for the INR, which has pushed up its value against the USD.
- Foreign direct investment: India has received a significant amount of foreign direct investment in recent years, which has also contributed to the appreciation of the INR.
- RBI intervention: The RBI has intervened in the foreign exchange market to stabilize the INR, which has helped to prevent its further depreciation.
- Global economic conditions: The global economic outlook can also have an impact on the USD/INR exchange rate. For example, a strong global economy can lead to increased demand for the USD, which can push up its value against the INR.
Future Prospects
The future prospects for the USD/INR exchange rate are uncertain. However, there are a number of factors that could lead to further appreciation of the INR. India’s strong economic growth is expected to continue in the coming years, which will lead to increased demand for the INR. Additionally, India is expected to attract more foreign direct investment in the coming years, which will also contribute to the appreciation of the INR.
However, there are also a number of factors that could lead to depreciation of the INR. The global economy could slow down, which would reduce demand for the USD and lead to a depreciation of the INR. Additionally, India could face a number of economic challenges in the coming years, such as inflation and a widening current account deficit. These challenges could also lead to depreciation of the INR.
Strategies for Managing Currency Risk
Businesses and individuals can implement a number of strategies to manage currency risk. These strategies include:
- Hedging: Hedging involves using financial instruments to offset the risk of currency fluctuations. There are a number of different hedging instruments available, such as forward contracts, options, and currency swaps.
- Diversification: Diversification involves investing in a variety of currencies to reduce the risk of exposure to any one currency.
- Natural hedging: Natural hedging involves using the natural flow of cash between different currencies to offset the risk of currency fluctuations.
Tips and Tricks
Here are a few tips for managing currency risk:
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date on the latest economic news and developments that could impact the USD/INR exchange rate.
- Use hedging instruments: Consider using hedging instruments to offset the risk of currency fluctuations.
- Diversify your investments: Invest in a variety of currencies to reduce the risk of exposure to any one currency.
- Use natural hedging: Use the natural flow of cash between different currencies to offset the risk of currency fluctuations.
Pros and Cons of Investing in the USD
There are a number of advantages and disadvantages to investing in the USD.
Advantages:
- The USD is the world’s reserve currency: This means that the USD is widely accepted and can be used to purchase goods and services all over the world.
- The USD is a safe haven currency: In times of economic uncertainty, investors often flock to the USD, which can lead to an appreciation of the USD against other currencies.
- The USD has a long history of stability: The USD has been the world’s reserve currency for over a century, and it has a long history of stability.
Disadvantages:
- The USD can lose value: The USD can lose value against other currencies, especially during periods of economic uncertainty.
- The USD can be affected by global economic conditions: The USD can be affected by global economic conditions, such as a slowdown in the global economy.
- The USD can be subject to government intervention: The USD can be subject to government intervention, such as interest rate changes or currency controls.
Market Insights and Future Trends
The USD/INR exchange rate is a key indicator of the health of the Indian economy. In recent years, the INR has appreciated against the USD, which has been driven by India’s strong economic growth and rising foreign direct investment. However, the future prospects for the USD/INR exchange rate are uncertain. A number of factors could lead to further appreciation of the INR, such as continued strong economic growth and increased foreign direct investment. However, there are also a number of factors that could lead to depreciation of the INR, such as a slowdown in the global economy or a widening current account deficit.
Conclusion
The USD/INR exchange rate is a complex and dynamic issue that is influenced by a number of factors. Businesses and individuals should be aware of the factors that influence the exchange rate and implement strategies to manage currency risk.
Appendix
Table 1: USD/INR Exchange Rate Historical Data
| Year | USD/INR |
|---|---|
| 1990 | 25.3 |
| 1995 | 32.4 |
| 2000 | 44.9 |
| 2005 | 43.7 |
| 2010 | 45.3 |
| 2015 | 63.5 |
| 2020 | 73.4 |
| 2022 | 79.3 |
Table 2: Factors Influencing the USD/INR Exchange Rate
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Economic growth | A strong economy leads to increased demand for the currency, which can push up its value. |
| Foreign direct investment | Foreign direct investment can lead to increased demand for the currency, which can push up its value. |
| Inflation | High inflation can erode the value of the currency, which can lead to its depreciation. |
| Interest rates | Higher interest rates can attract foreign investment, which can push up the value of the currency. |
| Political stability | Political instability can lead to uncertainty and a flight from the currency, which can push down its value. |
Table 3: Strategies for Managing Currency Risk
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Hedging | Using financial instruments to offset the risk of currency fluctuations. |
| Diversification | Investing in a variety of currencies to reduce the risk of exposure to any one currency. |
| Natural hedging | Using the natural flow of cash between different currencies to offset the risk of currency fluctuations. |
Table 4: Advantages and Disadvantages of Investing in the USD
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
| The USD is the world’s reserve currency | The USD can lose value |
| The USD is a safe haven currency | The USD can be affected by global economic conditions |
| The USD has a long history of stability | The USD can be subject to government intervention |