Introduction
The USD/KRW exchange rate is a key indicator of the relative value of the US dollar (USD) and the South Korean won (KRW). It plays a crucial role in international trade, investment, and tourism between the two countries. Understanding the factors that influence this exchange rate is essential for businesses, investors, and individuals involved in these activities.

Historical Trends
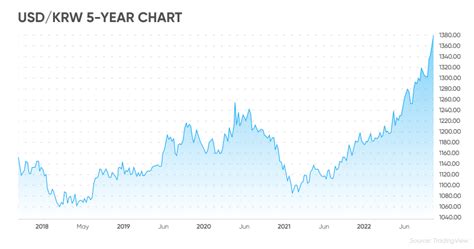
Over the past decade, the USD/KRW exchange rate has fluctuated significantly. In 2012, one USD was worth approximately 1,100 KRW. By 2015, this had climbed to over 1,250 KRW. However, in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, the exchange rate plunged to around 1,100 KRW in early 2020.
Factors Influencing the Exchange Rate
Numerous factors influence the USD/KRW exchange rate, including:
- Economic growth: Strength in the South Korean economy relative to the US economy tends to drive up the value of the KRW against the USD.
- Inflation: Higher inflation in South Korea than in the US can lead to a depreciation of the KRW against the USD.
- Interest rates: Interest rate differentials between the two countries can also affect the exchange rate. Higher interest rates in the US tend to make USD more attractive to investors.
- Political and geopolitical factors: Political and geopolitical uncertainties can impact market sentiment towards both currencies.
Current Status and Outlook
As of July 2023, one USD is worth approximately 1,235 KRW. This reflects a slight appreciation of the KRW against the USD in recent months.
The outlook for the USD/KRW exchange rate over the next two years remains uncertain. However, several factors suggest that the KRW may continue to strengthen against the USD:
- The South Korean economy is expected to continue growing at a faster pace than the US economy.
- Inflation in South Korea is projected to remain relatively low.
- The Bank of Korea is likely to maintain a hawkish stance on interest rates.
Impact on Businesses and Individuals
Fluctuations in the USD/KRW exchange rate can have significant implications for businesses and individuals:
- Businesses: Exporters in South Korea benefit from a stronger KRW, as their products become more affordable in overseas markets. Importers, on the other hand, may face higher costs if the KRW weakens against the USD.
- Individuals: Travelers from South Korea will find their money goes further in the US if the KRW appreciates against the USD. Conversely, travelers from the US to South Korea will experience a higher cost of living if the KRW depreciates.
Strategies to Mitigate Currency Risk
Businesses and individuals can adopt various strategies to mitigate currency risk:
- Hedging: Using financial instruments such as forward contracts or options to fix a future exchange rate.
- Diversification: Holding assets in multiple currencies to spread the risk.
- Local sourcing: Sourcing goods and services locally to reduce exposure to exchange rate fluctuations.
Conclusion
The USD/KRW exchange rate is a dynamic indicator influenced by a complex interplay of economic, financial, and geopolitical factors. Understanding the factors that drive this exchange rate and its potential impact is crucial for businesses and individuals involved in international trade, investment, and tourism. By adopting appropriate strategies, it is possible to mitigate currency risk and capitalize on favorable exchange rate movements.
Tables
| Year | USD/KRW Exchange Rate |
|---|---|
| 2012 | 1,100 |
| 2015 | 1,250 |
| 2020 | 1,100 |
| 2023 (July) | 1,235 |
| Factor | Impact on USD/KRW Exchange Rate |
|---|---|
| Economic growth | Stronger KRW if South Korea’s economy grows faster than the US economy |
| Inflation | Depreciation of KRW if inflation in South Korea is higher than in the US |
| Interest rates | Appreciation of USD if interest rates in the US are higher than in South Korea |
| Political and geopolitical factors | Can impact market sentiment towards both currencies, leading to fluctuations |
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Hedging | Using financial instruments to fix a future exchange rate |
| Diversification | Holding assets in multiple currencies |
| Local sourcing | Sourcing goods and services locally |