Understanding the USD-EUR Exchange Rate
The exchange rate between the US dollar (USD) and the euro (EUR) is a critical metric that impacts global trade, investment, and currency markets. The value of the USD relative to the EUR can significantly influence the competitiveness of exports, the attractiveness of investment opportunities, and the purchasing power of consumers.

Historical Trends and Market Dynamics
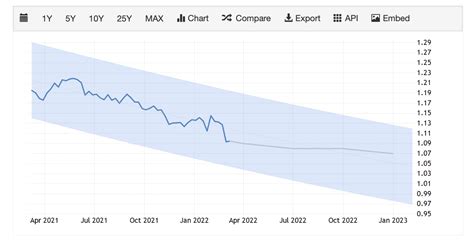
Over the past decade, the USD-EUR exchange rate has exhibited a volatile trend. In 2011, the EUR reached an all-time high of 1.5194 against the USD, fueled by the eurozone’s economic resilience compared to the struggling US economy. However, the euro’s strength waned over the following years as the European debt crisis and the subsequent recession weakened investor confidence.
In 2020, the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic further impacted the exchange rate, leading to a surge in the USD’s value relative to the EUR. This was driven by the perceived safe-haven status of the USD during periods of economic uncertainty.
2025 Projections and Economic Forecasts
Looking ahead, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projects that the USD-EUR exchange rate will average around 1.16 in 2025. This forecast takes into account several key factors, including:
- Economic growth: The IMF expects the US economy to recover from the COVID-19 pandemic and grow at a faster pace than the eurozone in the coming years.
- Interest rate differentials: The US Federal Reserve is projected to maintain a more accommodative monetary policy than the European Central Bank, leading to a wider interest rate spread and supporting the USD.
- US dollar dominance: The USD remains the world’s dominant reserve currency, providing stability and hedging opportunities for investors.
Impacts and Implications
The USD-EUR exchange rate has significant implications for various sectors:
Business:
- Exports: A stronger USD makes US exports more expensive, potentially negatively impacting trade competitiveness.
- Imports: A weaker USD makes imports from Europe cheaper, benefiting consumers and businesses that rely on imported goods.
- Investment: Companies may reassess investment decisions based on the cost of capital in different currency zones.
Individuals:
- Travel: A weaker USD will increase the purchasing power of Americans traveling in Europe, while a stronger USD will make European travel more expensive.
- Remittances: Individuals sending money to Europe from the US will receive more EUR for each USD if the USD is stronger.
- Savings: The exchange rate can impact the value of savings held in different currencies.
Central Banks:
- Monetary policy: Central banks may adjust monetary policies to influence the exchange rate, aiming to achieve economic objectives.
- Reserve management: Central banks hold a portion of their reserves in foreign currencies, and the USD-EUR exchange rate affects the value of these reserves.
Opportunities and Applications
The dynamic nature of the USD-EUR exchange rate presents opportunities for investors and businesses alike:
Investors:
- Currency trading: Traders can speculate on the movements of the USD-EUR exchange rate to seek profit.
- Hedging: Investors can use currency derivatives to protect against the fluctuations of the exchange rate.
- Multi-currency bonds: Bonds issued in different currencies can offer diversification and potential returns based on exchange rate movements.
Businesses:
- Currency risk management: Businesses exposed to currency fluctuations can develop strategies to mitigate risks.
- Export strategies: Companies can adjust their export strategies based on the exchange rate to optimize competitiveness.
- Global growth: The USD-EUR exchange rate can influence investment decisions and global expansion plans.
Conclusion
The USD-EUR exchange rate is a complex and ever-evolving metric that impacts various sectors of the economy. Understanding the historical trends, market dynamics, and 2025 projections is crucial for businesses and individuals to navigate the currency landscape effectively. By leveraging opportunities and managing risks associated with exchange rate fluctuations, stakeholders can maximize the benefits and minimize the challenges presented by the ever-changing USD-EUR relationship.
Tables
| Year | USD-EUR Exchange Rate |
|---|---|
| 2011 | 1.5194 |
| 2015 | 1.0389 |
| 2020 | 1.0767 |
| 2025 (Projected) | 1.16 |
| Country | Currency | Exchange Rate (as of March 8, 2023) |
|---|---|---|
| United States | US dollar | 1 |
| European Union | Euro | 1.0579 |
| United Kingdom | British pound | 0.8310 |
| Japan | Japanese yen | 133.09 |
| China | Chinese yuan | 6.9478 |
| Sector | Impact |
|---|---|
| Business | Exports, imports, investment |
| Individuals | Travel, remittances, savings |
| Central Banks | Monetary policy, reserve management |
| Investors | Currency trading, hedging, diversification |
| Opportunity | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Currency trading | Profit potential |
| Hedging | Risk mitigation |
| Multi-currency bonds | Diversification, potential returns |
| Currency risk management | Reduced financial losses |
| Export strategies | Increased competitiveness |
| Global growth | Expanded opportunities |