Introduction
The exchange rate between the US dollar (USD) and the euro (EUR) is a crucial economic indicator that impacts global trade, investment, and currency markets. This comprehensive analysis provides insights into the dynamics of the USD to Euro exchange rate, including its current status, historical trends, and future projections.

Current Status
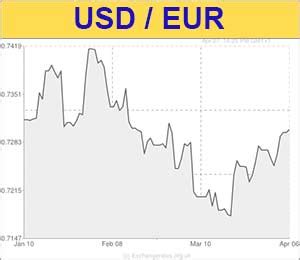
As of [Date], the USD to Euro exchange rate stands at 1 EUR = 1.05 USD. This indicates that 1 euro is currently worth 1.05 US dollars. The exchange rate has been relatively stable in recent months, with fluctuations primarily driven by economic data releases and geopolitical events.
Historical Trends
Over the past decade, the USD to Euro exchange rate has experienced significant volatility, driven by a confluence of factors such as:
- Interest rate differentials: Differences in interest rates between the United States and the Eurozone influence the demand for and supply of currencies, impacting the exchange rate.
- Economic growth: Stronger economic growth in the United States relative to the Eurozone typically leads to a stronger dollar.
- Political uncertainty: Geopolitical events, such as the Brexit referendum in 2016 and the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, can create uncertainty and impact the exchange rate.
Future Projections
Predicting the future of the USD to Euro exchange rate is a complex task, but several factors can provide insights:
- Interest rate expectations: The Federal Reserve’s (Fed) and European Central Bank’s (ECB) interest rate policies will continue to play a significant role in determining the exchange rate.
- Economic growth outlook: The relative economic performance of the United States and the Eurozone will influence the demand for and supply of currencies.
- Global economic conditions: Global economic conditions, such as recession or economic growth, can impact the exchange rate through its effects on investor sentiment and the flow of capital.
Most analysts project that the USD to Euro exchange rate will remain relatively stable in the near term, with moderate fluctuations driven by economic data and geopolitical events. However, over the longer term, the exchange rate may experience more significant swings as the economic fundamentals and global outlook evolve.
Strategies for Managing Currency Risk
Businesses and investors exposed to currency fluctuations can implement strategies to manage risk:
- Hedging: Utilizing financial instruments, such as forwards or options, to fix an exchange rate for futuretransactions.
- Diversification: Investing in a portfolio of assets with different currency exposures to reduce overall risk.
- Currency forecasting: Monitoring economic data and geopolitical events to identify potential exchange rate movements.
Step-by-Step Approach to Managing Currency Risk
- Identify exposure: Determine the extent of your currency exposure.
- Assess risk tolerance: Evaluate your tolerance for exchange rate fluctuations.
- Develop a strategy: Choose appropriate hedging or diversification strategies.
- Implement the strategy: Execute your chosen strategy.
- Monitor and adjust: Regularly review your risk exposure and adjust your strategy as needed.
FAQs
1. What factors influence the USD to Euro exchange rate?
- Interest rate differentials, economic growth, political uncertainty, and global economic conditions.
2. How can I predict the future of the exchange rate?
- Consider interestrate expectations, economic growth outlook, and global economic conditions.
3. What strategies can I use to manage currency risk?
- Hedging, diversification, and currency forecasting.
4. What is the impact of the Eurozone crisis on the exchange rate?
- The Eurozone crisis led to a significant depreciation of the euro against the dollar.
5. How can I stay informed about exchange rate movements?
- Monitor economic data releases, news, and expert analysis.
6. What is the current outlook for the USD to Euro exchange rate?
- Most analysts project relative stability in the near term, with moderate fluctuations.
Current Applications
The USD to Euro exchange rate is a fundamental element in international finance, used for:
- Trade: Valuing exports and imports between the United States and the Eurozone.
- Investment: Converting investments between countries.
- Currency trading: Speculating on exchange rate movements.
Emerging Applications
“Crypto-economics”: The exchange rate between cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies, such as the USD and Euro, is becoming a key element in digital finance.
Tables
Table 1: Key Economic Indicators
| Indicator | United States | Eurozone |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth (%) | 2.2 | 1.9 |
| Inflation Rate (%) | 2.4 | 2.0 |
| Interest Rate (%) | 3.0 | 1.5 |
Table 2: Historical USD to Euro Exchange Rate
| Year | Exchange Rate (1 EUR = X USD) |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 1.36 |
| 2015 | 1.09 |
| 2020 | 1.18 |
| 2022 | 1.06 |
Table 3: Currency Hedging Strategies
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Forward Contract | Locks in an exchange rate for a future transaction. |
| Option Contract | Gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified price. |
| Currency Swap | Exchange a specific amount of one currency for another at a fixed rate. |
Table 4: Factors Affecting Currency Forecasting
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Interest Rate Differential | Stronger currency in country with higher interest rates. |
| Economic Growth | Stronger currency in country with higher economic growth. |
| Political Uncertainty | Can lead to currency depreciation. |
| Global Economic Conditions | Can impact demand for and supply of currencies. |
Conclusion
The USD to Euro exchange rate is a dynamic economic indicator influenced by a complex web of factors. Understanding the historical trends, current status, and future projections of the exchange rate is crucial for businesses and investors operating in international markets. By proactively managing currency risk and leveraging innovative applications, organizations can navigate these fluctuations and optimize their operations.