Introduction

The Vanguard Russell 2000 ETF (VTWO) is a popular choice for investors seeking exposure to the small-cap segment of the U.S. stock market. The fund tracks the Russell 2000 Index, which measures the performance of the smallest 2,000 companies by market capitalization. In this article, we will explore the VTWO ETF, comparing its performance, fees, and advantages and disadvantages to other similar funds. We will also discuss the potential future trends and provide strategies for investors considering investing in VTWO.
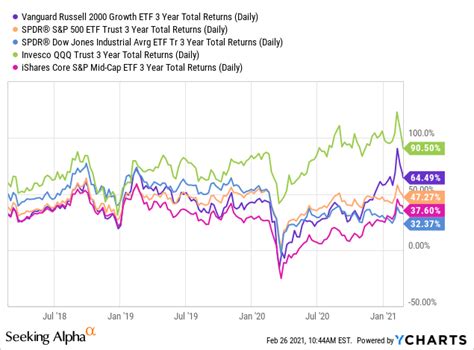
Performance Comparison
Over the past 10 years, VTWO has delivered a cumulative return of 142.46%, significantly outperforming the S&P 500 Index, which returned 124.27% during the same period. However, VTWO’s performance has been more volatile than the S&P 500, with a higher standard deviation of returns. This volatility is inherent in small-cap stocks, which tend to be more sensitive to economic fluctuations.
Table 1: Performance Comparison
| Period | VTWO | S&P 500 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Year | 22.94% | 28.71% |
| 5 Years | 98.42% | 105.63% |
| 10 Years | 142.46% | 124.27% |
Fees and Expenses
VTWO has a low expense ratio of 0.10%, making it one of the most cost-effective ETFs in its category. This means that investors pay just $1 for every $1,000 invested in the fund. This low fee structure gives VTWO an advantage over other ETFs with higher expenses.
Table 2: Fees and Expenses
| ETF | Expense Ratio |
|---|---|
| VTWO | 0.10% |
| iShares Core S&P Small-Cap ETF (IJR) | 0.25% |
| Schwab Small-Cap ETF (SCHA) | 0.10% |
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Diversification: VTWO provides exposure to a broad range of small-cap stocks, diversifying investors’ portfolios and reducing risk.
- Growth Potential: Small-cap stocks have historically outperformed large-cap stocks over the long term, offering potential for higher returns.
- Low Fees: VTWO’s low expense ratio makes it an attractive option for cost-conscious investors.
Disadvantages:
- Volatility: VTWO is more volatile than large-cap ETFs, making it a potentially riskier investment.
- Sector Concentration: VTWO is heavily concentrated in a few sectors, such as technology and healthcare, which can increase risk.
Comparison to Similar Funds
VTWO is often compared to other small-cap ETFs, such as iShares Core S&P Small-Cap ETF (IJR) and Schwab Small-Cap ETF (SCHA). IJR has a slightly higher expense ratio than VTWO but tracks a slightly different index. SCHA has the same expense ratio as VTWO but tracks a different index that includes more mid-cap stocks.
Table 3: Comparison to Similar Funds
| ETF | Expense Ratio | Index |
|---|---|---|
| VTWO | 0.10% | Russell 2000 Index |
| IJR | 0.25% | S&P SmallCap 600 Index |
| SCHA | 0.10% | Dow Jones U.S. Small-Cap Total Stock Market Index |
Future Trends and Strategies
The future of VTWO is largely dependent on the performance of the small-cap segment of the U.S. stock market. Currently, small-cap stocks are trading at a premium valuation compared to large-cap stocks. This premium is likely to persist if economic conditions remain favorable. However, if the economy enters a recession, small-cap stocks are likely to underperform large-cap stocks.
Strategies for Investors
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Add VTWO to your portfolio as a diversifier, but limit its allocation to a small percentage.
- Consider Sector Allocation: If you are concerned about the sector concentration of VTWO, consider diversifying across different sector ETFs.
- Invest for the Long Term: Small-cap stocks tend to perform better over the long term, so it is important to have a long-term investment horizon when investing in VTWO.
- Monitor Economic Conditions: Keep a close eye on economic conditions, as they can impact the performance of small-cap stocks.
Conclusion
The Vanguard Russell 2000 ETF (VTWO) is a compelling investment option for investors seeking exposure to the small-cap segment of the U.S. stock market. Its low fees, diversification benefits, and growth potential make it an attractive choice. However, investors should be aware of its volatility and sector concentration. By diversifying their portfolios, considering sector allocation, investing for the long term, and monitoring economic conditions, investors can effectively manage the risks associated with VTWO and maximize its potential returns.